Acute Pancreatitis due to pH-Dependent Mesalazine That Occurred in the Course of Ulcerative Colitis
- PMID: 22110423
- PMCID: PMC3219486
- DOI: 10.1159/000333605
Acute Pancreatitis due to pH-Dependent Mesalazine That Occurred in the Course of Ulcerative Colitis
Abstract
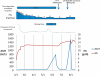
We report the case of a 26-year-old male who presented with acute pancreatitis during the course of treatment for pancolitic ulcerative colitis (UC) with a time-dependent mesalazine formulation, prednisolone and azathioprine (AZA). Despite a review of his clinical history and various tests, the cause of pancreatitis could not be determined. Since drug-induced pancreatitis was considered possible, administration of the time-dependent mesalazine preparation and AZA was discontinued, and conservative treatment for acute pancreatitis was performed. The pancreatitis promptly improved with these treatments, but drug lymphocyte stimulation test (DLST) for both the time-dependent mesalazine formulation and AZA was negative. A pH-dependent mesalazine formulation was given for maintenance therapy of UC. Subsequently, as the pancreatitis relapsed, drug-induced pancreatitis was strongly suspected. Administration of mesalazine was discontinued, and pancreatitis was smoothly in remission by conservative treatment. According to the positive DLST result for the pH-dependent mesalazine formulation and the clinical course, a diagnosis of pH-dependent mesalazine-induced pancreatitis due to this formulation was made. During the clinical course of UC, occurrence of drug-induced pancreatitis must always be considered.
Keywords: Mesalazine; Pancreatitis; Ulcerative colitis.
Figures


References
-
- Weber P, Seibold F, Jenss H. Acute pancreatitis in Crohn's disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1993;17:286–291. - PubMed
-
- Raumussen HH, Fonager K, Sorensen HT, et al. Risk of acute pancreatitis in patients with chronic inflammatory bowel disease. A Danish 16-year nationwide follow-up study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1999;34:199–201. - PubMed
-
- Adachi E, Okazaki K, Matsushima Y, et al. Acute pancreatitis secondary to 5-aminosalicylic acid therapy in a patient with ulcerative colitis. Int J Pancreatol. 1999;25:217–221. - PubMed
-
- Kurose I, Miura S, Suematsu M, et al. Tissue-type plasminogen activator of colonic mucosa in ulcerative colitis. Evidence of endothelium-derived fibrinolytic activation. Dig Dis Sci. 1992;37:307–311. - PubMed
-
- Frey CY. Acute pancreatitis as a complication of ulcerative colitis and collagen disease. Univ Mich Med Cent J. 1967;33:18–21. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

