Adolescent oxytocin exposure causes persistent reductions in anxiety and alcohol consumption and enhances sociability in rats
- PMID: 22110618
- PMCID: PMC3217952
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027237
Adolescent oxytocin exposure causes persistent reductions in anxiety and alcohol consumption and enhances sociability in rats
Abstract
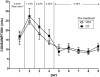
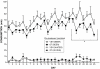
Previous studies have suggested that administration of oxytocin (OT) can have modulatory effects on social and anxiety-like behavior in mammals that may endure beyond the time of acute OT administration. The current study examined whether repeated administration of OT to male Wistar rats (n = 48) during a key developmental epoch (early adolescence) altered their physiology and behavior in later-life. Group housed rats were given intraperitoneal injections of either 1 mg/kg OT or vehicle during early adolescence (post natal-days [PND] 33-42). OT treatment caused a transient inhibition of body weight gain that recovered quickly after the cessation of treatment. At PND 50, the rats pre-treated with OT displayed less anxiety-like behavior on the emergence test, while at PND 55 they showed greater levels of social interaction. A subgroup of OT pre-treated rats examined at PND 63 showed a strong trend towards increased plasma OT levels, and also displayed significantly increased OT receptor mRNA in the hypothalamus. Rats pre-treated with OT and their controls showed similar induction of beer intake in daily 70 min test sessions (PND 63 onwards) in which the alcohol concentration of beer was gradually increased across days from 0.44% to 4.44%. However, when given ad libitum access to beer in their home cages from PND 72 onwards (early adulthood), consumption of beer but not water was significantly less in the OT pre-treated rats. A "booster" shot of OT (1 mg/kg) given after 25 days of ad libitum access to beer had a strong acute inhibitory effect on beer intake without affecting water intake. Overall these results suggest that exogenous OT administered during adolescence can have subtle yet enduring effects on anxiety, sociability and the motivation to consume alcohol. Such effects may reflect the inherent neuroplasticity of brain OT systems and a feed-forward effect whereby exogenous OT upregulates endogenous OT systems.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

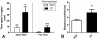
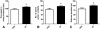
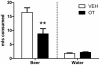
References
-
- Francis DD, Young LJ, Meaney MJ, Insel TR. Naturally occurring differences in maternal care are associated with the expression of oxytocin and vasopressin (v1a) receptors: Gender differences. J Neuroendocrinol. 2002;14:349–353. - PubMed
-
- Neumann ID. Brain oxytocin: A key regulator of emotional and social behaviours in both females and males. J Neuroendocrinol. 2008;20:858–865. - PubMed
-
- Young LJ. The neurobiology of social recognition, approach, and avoidance. Biol Psychiatry. 2002;51:18–26. - PubMed
-
- Lukas M, Toth I, Reber SO, Slattery DA, Veenema AH, et al. The neuropeptide oxytocin facilitates pro-social behavior and prevents social avoidance in rats and mice. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011 doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.95. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

