Astragalus polysaccharides lowers plasma cholesterol through mechanisms distinct from statins
- PMID: 22110652
- PMCID: PMC3217967
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027437
Astragalus polysaccharides lowers plasma cholesterol through mechanisms distinct from statins
Abstract
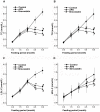
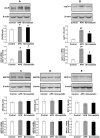
To determine the efficacy and underlying mechanism of Astragalus polysaccharides (APS) on plasma lipids in hypercholesterolemia hamsters. The effect of APS (0.25 g/kg/d) on plasma and liver lipids, fecal bile acids and neutral sterol, cholesterol absorption and synthesis, HMG-CoA reductase activity, and gene and protein expressions in the liver and small intestine was investigated in twenty-four hypercholesterolemia hamsters. Treatment periods lasted for three months. APS significantly lowered plasma total cholesterol by 45.8%, triglycerides by 30%, and low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol by 47.4%, comparable to simvastatin. Further examinations revealed that APS reduced total cholesterol and triglycerides in the liver, increased fecal bile acid and neutral sterol excretion, inhibited cholesterol absorption, and by contrast, increased hepatic cholesterol synthesis and HMG-CoA reductase activity. Plasma total cholesterol or low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels were significantly correlated with cholesterol absorption rates. APS up-regulated cholesterol-7α-hydroxylase and LDL-receptor gene expressions. These new findings identify APS as a potential natural cholesterol lowering agent, working through mechanisms distinct from statins.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Collins R, Armitage J, Parish s, Sleight P, Peto R, et al. MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of cholesterol lowering with simvastatin in 20,536 high-risk individuals: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;360:7–22. - PubMed
-
- Lenfant C, Cleeman JI, Ganiats TG, Graham G, Kleinman RE, et al. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA. 2001;285:2486–2497. - PubMed
-
- Huang X, Wang D, Hu Y, Lu Y, Guo Z, et al. Effect of sulfated astragalus polysaccharide on cellular infectivity of infectious bursal disease virus. Int J Biol Macromol. 2008;42:166–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

