Serum IgA responses against pertussis proteins in infected and Dutch wP or aP vaccinated children: an additional role in pertussis diagnostics
- PMID: 22110718
- PMCID: PMC3215732
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027681
Serum IgA responses against pertussis proteins in infected and Dutch wP or aP vaccinated children: an additional role in pertussis diagnostics
Abstract
Background: Whooping cough is a respiratory disease caused by Bordetella pertussis, which induces mucosal IgA antibodies that appear to be relevant in protection. Serum IgA responses are measured after pertussis infection and might provide an additional role in pertussis diagnostics. However, the possible interfering role for pertussis vaccinations in the induction of serum IgA antibodies is largely unknown.
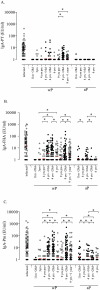
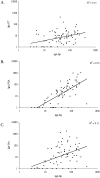
Methods/principal findings: We compared serum IgA responses in healthy vaccinated children between 1 and 10 years of age with those in children who despite vaccinations recently were infected with Bordetella pertussis. All children have been vaccinated at 2, 3, 4 and 11 months of age with either the Dutch whole-cell pertussis (wP) vaccine or an acellular pertussis (aP) vaccine and additionally received an aP booster vaccination at 4 years of age. Serum IgA responses to pertussis toxin (PT), filamentous heamagglutinin (FHA) and pertactin (Prn) were measured with a fluorescent multiplex bead-based immuno-assay. An ELISPOT-assay was used for the detection of IgA-memory B-cells specific to these antigens. Serum IgA levels to all pertussis vaccine antigens were significantly higher in infected children compared with healthy children. High correlations between anti-PT, anti-FHA or anti-Prn IgA and IgG levels were found in infected children and to some degree in wP primed children, but not at all in aP primed children. Highest numbers of IgA-pertussis-specific memory B-cells were observed after infection and generally comparable numbers were found after wP and aP vaccination.
Conclusions: This study provides new insight in the diagnostic role for serum IgA responses against PT in vaccinated children. Since aP vaccines induce high serum IgG levels that interfere with pertussis diagnostics, serum IgA-PT levels will provide an additional diagnostic role. High levels of serum IgA for PT proved specific for recent pertussis infection with reasonable sensitivity, whereas the role for IgA levels against FHA and Prn in diagnosing pertussis remains controversial.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Parton R. Review of the biology of Bordetella pertussis. Biologicals. 1999;27:71–76. - PubMed
-
- Woof JM, Kerr MA. The function of immunoglobulin A in immunity. J Pathol. 2006;208:270–282. - PubMed
-
- Nagel J, Poot-Scholtens EJ. Serum IgA antibody to Bordetella pertussis as an indicator of infection. J Med Microbiol. 1983;16:417–426. - PubMed
-
- Novotny P, Macaulay ME, Hart TC, Skvaril F. Analysis of antibody profiles in children with whooping cough. Dev Biol Stand. 1991;73:267–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

