Assessment of daily life physical activities in pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 22110770
- PMCID: PMC3218075
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027993
Assessment of daily life physical activities in pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
Background: In pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), the six-minute walk test (6MWT) is believed to be representative of patient's daily life physical activities (DL(PA)). Whether DL(PA) are decreased in PAH and whether the 6MWT is representative of patient's DL(PA) remain unknown.
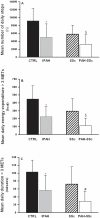
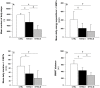
Methods: 15 patients with idiopathic PAH (IPAH) and 10 patients with PAH associated with limited systemic sclerosis (PAH-SSc) were matched with 15 healthy control subjects and 10 patients with limited systemic sclerosis without PAH. Each subject completed a 6MWT. The mean number of daily steps and the mean energy expenditure and duration of physical activities >3 METs were assessed with a physical activity monitor for seven consecutive days and used as markers of DL(PA).
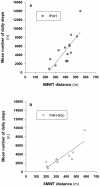
Results: The mean number of daily steps and the mean daily energy expenditure and duration of physical activities >3 METs were all reduced in PAH patients compared to their controls (all p<0.05). The mean number of daily steps correlated with the 6MWT distance for both IPAH and PAH-SSc patients (r = 0.76, p<0.01 and r = 0.85, p<0.01), respectively.
Conclusion: DL(PA) are decreased in PAH and correlate with the 6MWT distance. Functional exercise capacity may thus be a useful surrogate of DL(PA) in PAH.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Groepenhoff H, Vonk-Noordegraaf A, Boonstra A, Spreeuwenberg MD, Postmus PE, et al. Exercise testing to estimate survival in pulmonary hypertension. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008;40:1725–1732. - PubMed
-
- Miyamoto S, Nagaya N, Satoh T, Kyotani S, Sakamaki F, et al. Clinical correlates and prognostic significance of six-minute walk test in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Comparison with cardiopulmonary exercise testing. AmJRespirCrit Care Med. 2000;161:487–492. - PubMed
-
- Provencher S. Long-term treprostinil in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Is the glass half full or half empty? EurRespir J. 2006;28:1073–1075. - PubMed
-
- Sitbon O, Humbert M, Nunes H, Parent F, Garcia G, et al. Long-term intravenous epoprostenol infusion in primary pulmonary hypertension: prognostic factors and survival. JAmCollCardiol. 2002;40:780–788. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

