Semiconductor quantum dots as fluorescent probes for in vitro and in vivo bio-molecular and cellular imaging
- PMID: 22110865
- PMCID: PMC3215221
- DOI: 10.3402/nano.v1i0.5161
Semiconductor quantum dots as fluorescent probes for in vitro and in vivo bio-molecular and cellular imaging
Abstract
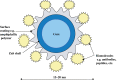
Over the years, biological imaging has seen many advances, allowing scientists to unfold many of the mysteries surrounding biological processes. The ideal imaging resolution would be in nanometres, as most biological processes occur at this scale. Nanotechnology has made this possible with functionalised nanoparticles that can bind to specific targets and trace processes at the cellular and molecular level. Quantum dots (QDs) or semiconductor nanocrystals are luminescent particles that have the potential to be the next generation fluorophores. This paper is an overview of the basics of QDs and their role as fluorescent probes for various biological imaging applications. Their potential clinical applications and the limitations that need to be overcome have also been discussed.
Keywords: in vitro and in vivo imaging; quantum dots.
Figures





References
-
- West JL, Halas NJ. Applications of nanotechnology to biotechnology commentary. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2000;11:215–7. - PubMed
-
- Rossetti R, Brus L. Electron-hole recombination emission as a probe of surface-chemistry in aqueous CdS colloids. J Phys Chem. 1982;86:4470–2.
-
- Alivisatos AP. Birth of a nanoscience building block. ACS Nano. 2008;2:1514–6. - PubMed
-
- Weller H. Colloidal semiconductor Q-particles - chemistry in the transition region between solid-state and molecules. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng. 1993;32:41–53.
-
- Murray CB, Norris DJ, Bawendi MG. Synthesis and characterization of nearly monodisperse Cde (e=S, Se, Te) semiconductor nanocrystallites. J Am Chem Soc. 1993;115:8706–15.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
