Hybrid micro-/nanogels for optical sensing and intracellular imaging
- PMID: 22110866
- PMCID: PMC3215222
- DOI: 10.3402/nano.v1i0.5730
Hybrid micro-/nanogels for optical sensing and intracellular imaging
Abstract
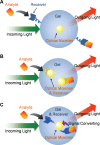
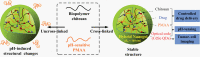
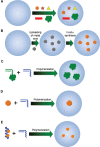
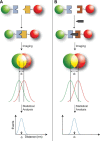
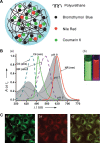
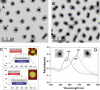
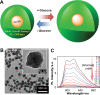
Hybrid micro-/nanogels are playing an increasing important part in a diverse range of applications, due to their tunable dimensions, large surface area, stable interior network structure, and a very short response time. We review recent advances and challenges in the developments of hybrid micro-/nanogels toward applications for optical sensing of pH, temperature, glucose, ions, and other species as well as for intracellular imaging. Due to their unique advantages, hybrid micro-/nanogels as optical probes are attracting substantial interests for continuous monitoring of chemical parameters in complex samples such as blood and bioreactor fluids, in chemical research and industry, and in food quality control. In particular, their intracellular probing ability enables the monitoring of the biochemistry and biophysics of live cells over time and space, thus contributing to the explanation of intricate biological processes and the development of novel diagnoses. Unlike most other probes, hybrid micro-/nanogels could also combine other multiple functions into a single probe. The rational design of hybrid micro-/nanogels will not only improve the probing applications as desirable, but also implement their applications in new arenas. With ongoing rapid advances in bionanotechnology, the well-designed hybrid micro-/nanogel probes will be able to provide simultaneous sensing, imaging diagnosis, and therapy toward clinical applications.
Keywords: cell imaging; hybrids; intracellular detection; microgel; nanogel; optical biosensor; stimuli-responsive polymer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Responsive polymer-fluorescent carbon nanoparticle hybrid nanogels for optical temperature sensing, near-infrared light-responsive drug release, and tumor cell imaging.Nanoscale. 2014 Jul 7;6(13):7443-52. doi: 10.1039/c4nr01030b. Nanoscale. 2014. PMID: 24881520
-
An insight of nanogels as novel drug delivery system with potential hybrid nanogel applications.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2022 Feb;33(2):262-278. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2021.1982643. Epub 2021 Oct 10. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2022. PMID: 34547214
-
Carbon-based hybrid nanogels: a synergistic nanoplatform for combined biosensing, bioimaging, and responsive drug delivery.Chem Soc Rev. 2018 Jun 5;47(11):4198-4232. doi: 10.1039/c7cs00399d. Chem Soc Rev. 2018. PMID: 29667656 Review.
-
Chitosan-based responsive hybrid nanogels for integration of optical pH-sensing, tumor cell imaging and controlled drug delivery.Biomaterials. 2010 Nov;31(32):8371-81. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.07.061. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Biomaterials. 2010. PMID: 20701965
-
Recent developments in stimuli-responsive polymer nanogels for drug delivery and diagnostics: A review.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020 Dec;157:121-153. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.10.009. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020. PMID: 33091554 Review.
Cited by
-
A Visual Distance-Based Capillary Immunoassay Using Biomimetic Polymer Nanoparticles for Highly Sensitive and Specific C-Reactive Protein Quantification.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 10;25(18):9771. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189771. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337259 Free PMC article.
-
Nanogels as imaging agents for modalities spanning the electromagnetic spectrum.Mater Horiz. 2016 Jan 21;3(1):21-40. doi: 10.1039/c5mh00161g. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Mater Horiz. 2016. PMID: 27398218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology for Neuroscience: Promising Approaches for Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Brain Activity Mapping.Adv Funct Mater. 2017 Oct 19;27(39):1700489. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201700489. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Adv Funct Mater. 2017. PMID: 30853878 Free PMC article.
-
Bioengineering Microgels and Hydrogel Microparticles for Sensing Biomolecular Targets.Gels. 2017 May 30;3(2):20. doi: 10.3390/gels3020020. Gels. 2017. PMID: 30920517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Developments in Medical Applications of Hybrid Hydrogels Containing Natural Polymers.Molecules. 2020 Mar 27;25(7):1539. doi: 10.3390/molecules25071539. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32230990 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hoffman AS. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2002;43:3–12. - PubMed
-
- Nayak S, Lyon LA. Soft nanotechnology with soft nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2005;44:7686–708. - PubMed
-
- Peppas NA, Hilt JZ, Khademhosseini A, Langer R. Hydrogels in biology and medicine: from molecular principles to bionanotechnology. Adv Mater. 2006;18:1345–60.
-
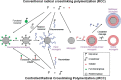
- Sanson N, Rieger J. Synthesis of nanogels/microgels by conventional and controlled radical crosslinking copolymerization. Polym Chem. 2010;1:965–77.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
