Assessment of procalcitonin to predict outcome in hypothermia-treated patients after cardiac arrest
- PMID: 22110909
- PMCID: PMC3205599
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/631062
Assessment of procalcitonin to predict outcome in hypothermia-treated patients after cardiac arrest
Abstract
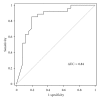
Objective. Determine the potential of procalcitonin (PCT) to predict neurological outcome after hypothermia treatment following cardiac arrest. Methods. Retrospective analysis of patient data over a 2-year period. Mortality and neurological outcome of survivors were determined 6 months after cardiac arrest using the Cerebral Performance Category (CPC) score. Results. Data from 53 consecutive patients were analyzed. Median age was 63 (54-71) and 79% were male. Twenty-seven patients had good outcome (CPC ≤ 2) whereas 26 had severe neurological sequelae or died (CPC 3-5). At 48 h, after regaining normothermia, PCT was significantly higher in patients with bad outcome compared to those with good outcome: 3.38 (1.10-24.48) versus 0.28 (0-0.75) ng/mL (P < 0.001). PCT values correlated with bad neurological outcome (r = 0.54, P = 0.00004) and predicted outcome with an area under the curve of 0.84 (95% CI 0.73-0.96). A cutoff point of 1 ng/mL provided a sensitivity of 85% and a specificity of 81%. Above a PCT level of 16 ng/mL, no patient regained consciousness. PCT provided an additive value over simplified acute physiology score II. Conclusions. PCT might be an ancillary marker for outcome prediction after cardiac arrest treated by induced hypothermia.
Figures
References
-
- Adrie C, Adib-Conquy M, Laurent I, et al. Successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation after cardiac arrest as a “sepsis-like” syndrome. Circulation. 2002;106(5):562–568. - PubMed
-
- Bouadma L, Luyt CE, Tubach F, et al. Use of procalcitonin to reduce patients’ exposure to antibiotics in intensive care units (PRORATA trial): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. The Lancet. 2010;375(9713):463–474. - PubMed
-
- Harbarth S, Holeckova K, Froidevaux C, et al. Diagnostic value of procalcitonin, interleukin-6, and interleukin-8 in critically ill patients admitted with suspected sepsis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2001;164(3):396–402. - PubMed
-
- Jensen JU, Heslet L, Jensen TH, Espersen K, Steffensen P, Tvede M. Procalcitonin increase in early identification of critically ill patients at high risk of mortality. Critical Care Medicine. 2006;34(10):2596–2602. - PubMed
-
- Mongardon N, Lemiale V, Perbet S, et al. Value of procalcitonin for diagnosis of early onset pneumonia in hypothermia-treated cardiac arrest patients. Intensive Care Medicine. 2010;36(1):92–99. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials