Characterization of Sucrose transporter alleles and their association with seed yield-related traits in Brassica napus L
- PMID: 22112023
- PMCID: PMC3248380
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-11-168
Characterization of Sucrose transporter alleles and their association with seed yield-related traits in Brassica napus L
Abstract
Background: Sucrose is the primary photosynthesis product and the principal translocating form within higher plants. Sucrose transporters (SUC/SUT) play a critical role in phloem loading and unloading. Photoassimilate transport is a major limiting factor for seed yield. Our previous research demonstrated that SUT co-localizes with yield-related quantitative trait loci. This paper reports the isolation of BnA7.SUT1 alleles and their promoters and their association with yield-related traits.
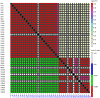
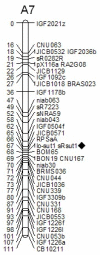
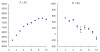
Results: Two novel BnA7.SUT1 genes were isolated from B. napus lines 'Eagle' and 'S-1300' and designated as BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b, respectively. The BnA7.SUT1 protein exhibited typical SUT features and showed high amino acid homology with related species. Promoters of BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b were also isolated and classified as pBnA7.SUT1.a and pBnA7.SUT1.b, respectively. Four dominant sequence-characterized amplified region markers were developed to distinguish BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b. The two genes were estimated as alleles with two segregating populations (F2 and BC1) obtained by crossing '3715'×'3769'. BnA7.SUT1 was mapped to the A7 linkage group of the TN doubled haploid population. In silico analysis of 55 segmental BnA7.SUT1 alleles resulted three BnA7.SUT1 clusters: pBnA7.SUT1.a- BnA7.SUT1.a (type I), pBnA7.SUT1.b- BnA7.SUT1.a (type II), and pBnA7.SUT1.b- BnA7.SUT1.b (type III). Association analysis with a diverse panel of 55 rapeseed lines identified single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in promoter and coding domain sequences of BnA7.SUT1 that were significantly associated with one of three yield-related traits: number of effective first branches (EFB), siliques per plant (SP), and seed weight (n = 1000) (TSW) across all four environments examined. SNPs at other BnA7.SUT1 sites were also significantly associated with at least one of six yield-related traits: EFB, SP, number of seeds per silique, seed yield per plant, block yield, and TSW. Expression levels varied over various tissue/organs at the seed-filling stage, and BnA7.SUT1 expression positively correlated with EFB and TSW.
Conclusions: Sequence, mapping, association, and expression analyses collectively showed significant diversity between the two BnA7.SUT1 alleles, which control some of the phenotypic variation for branch number and seed weight in B. napus consistent with expression levels. The associations between allelic variation and yield-related traits may facilitate selection of better genotypes in breeding.
© 2011 Li et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd.
Figures
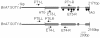

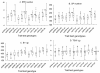
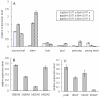
Similar articles
-
Exploring silique number in Brassica napus L.: Genetic and molecular advances for improving yield.Plant Biotechnol J. 2024 Jul;22(7):1897-1912. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14309. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Plant Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 38386569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative quantitative trait loci for silique length and seed weight in Brassica napus.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 23;5:14407. doi: 10.1038/srep14407. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26394547 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse regulatory factors associate with flowering time and yield responses in winter-type Brassica napus.BMC Genomics. 2015 Sep 29;16:737. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1950-1. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26419915 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative trait analysis of seed yield and other complex traits in hybrid spring rapeseed (Brassica napus L.): 1. Identification of genomic regions from winter germplasm.Theor Appl Genet. 2006 Aug;113(3):549-61. doi: 10.1007/s00122-006-0323-1. Epub 2006 Jun 10. Theor Appl Genet. 2006. PMID: 16767447
-
Quantitative trait loci analysis and genome-wide comparison for silique related traits in Brassica napus.BMC Plant Biol. 2016 Mar 22;16:71. doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0759-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 27000872 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring silique number in Brassica napus L.: Genetic and molecular advances for improving yield.Plant Biotechnol J. 2024 Jul;22(7):1897-1912. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14309. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Plant Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 38386569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unravelling the complex trait of harvest index in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) with association mapping.BMC Genomics. 2015 May 12;16(1):379. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1607-0. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25962630 Free PMC article.
-
Joint genome-wide association and transcriptome sequencing reveals a complex polygenic network underlying hypocotyl elongation in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.).Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 31;7:41561. doi: 10.1038/srep41561. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28139730 Free PMC article.
-
The long noncoding RNA Chaer defines an epigenetic checkpoint in cardiac hypertrophy.Nat Med. 2016 Oct;22(10):1131-1139. doi: 10.1038/nm.4179. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Nat Med. 2016. PMID: 27618650 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Fruit Shading on Gene and Protein Expression During Starch and Oil Accumulation in Developing Styrax tonkinensis Kernels.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 2;13:905633. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.905633. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35720550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weselake RJ. Storage Product Metabolism in Microspore-Derived Cultures of Brassicaceae. Biotech Agric For. 2005;56:97–122.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

