RNA-Seq reveals infection-related global gene changes in Phytophthora phaseoli, the causal agent of lima bean downy mildew
- PMID: 22112294
- PMCID: PMC6638658
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2011.00761.x
RNA-Seq reveals infection-related global gene changes in Phytophthora phaseoli, the causal agent of lima bean downy mildew
Abstract
Lima bean is an important vegetable processing crop to the mid-Atlantic USA and is highly susceptible to the oomycete pathogen Phytophthora phaseoli, which causes downy mildew. Genetic resistance and fungicides are used to manage P. phaseoli and often fail. Currently, the molecular basis of the interaction between this host and pathogen is unknown. To begin to rectify this situation, we used Illumina RNA-Seq to perform a global transcriptome analysis comparing P. phaseoli growing in culture with P. phaseoli infecting its host. Sequence reads from a total of six libraries mapped to gene models from the closely related late blight pathogen, Phytophthora infestans, resulting in 10 427 P. phaseoli genes with homology to P. infestans and expression in at least one library. Of these, 318 P. phaseoli homologues matched known or putative virulence genes in P. infestans. Two well-studied classes, RxLRs and elicitins, were up-regulated in planta, whereas the reverse was true for another class, called crinklers. These results are discussed with respect to the differences and similarities in the pathogenicity mechanisms of P. phaseoli and P. infestans.
© 2011 University Of Delaware. Molecular Plant Pathology © 2011 BSPP and Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
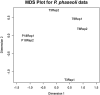
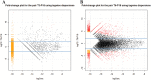
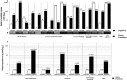



References
-
- App, F. (1959) The history and economic importance of lima bean downy mildew disease. Proc. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 33, 473–476.
-
- Armstrong, M.R. , Whisson, S.C. , Pritchard, L. , Bos, J.I. , Venter, E. , Avrova, A.O. , Rehmany, A.P. , Böhme, U. , Brooks, K. , Cherevach, I. , Hamlin, N. , White, B. , Fraser, A. , Lord, A. , Quail, M.A. , Churcher, C. , Hall, N. , Berriman, M. , Huang, S. , Kamoun, S. , Beynon, J.L. and Birch, P.R. (2005) An ancestral oomycete locus contains late blight avirulence gene Avr3a, encoding a protein that is recognized in the host cytoplasm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 102, 7766–7771. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asmann, Y.W. , Wallace, M.B. and Thompson, E.A. (2008) Transcriptome profiling using next‐generation sequencing. Gastroenterology, 135, 1466–1468. - PubMed
-
- Birch, P.R. , Rehmany, A.P. , Pritchard, L. , Kamoun, S. and Beynon, J.L. (2006) Trafficking arms: oomycete effectors enter host plant cells. Trends Microbiol. 14, 8–11. - PubMed
-
- Blair, J.E. , Coffey, M.D. , Park, S.‐Y. , Geiser, D.M. and Kang, S. (2008) A multi‐locus phylogeny for Phytophthora utilizing markers derived from complete genome sequences. Fungal Genet. Biol. 45, 266–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

