Low plasma level of atrial natriuretic peptide predicts development of diabetes: the prospective Malmo Diet and Cancer study
- PMID: 22112816
- PMCID: PMC3275360
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2011-2425
Low plasma level of atrial natriuretic peptide predicts development of diabetes: the prospective Malmo Diet and Cancer study
Abstract
Context: The cardiac natriuretic peptides are involved in blood pressure regulation, and large cross-sectional studies have shown lower plasma levels of N-terminal pro-natriuretic peptide levels [N-terminal atrial natriuretic peptide (N-ANP) and N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide (N-BNP)] in patients with insulin resistance, obesity, and diabetes.
Objective: In this study, we prospectively tested whether plasma levels of mid-regional ANP (MR-ANP) and N-BNP predict new-onset diabetes and long-term glucose progression.
Design, setting, and patients: MR-ANP and N-BNP were measured in 1828 nondiabetic individuals of the Malmö Diet and Cancer cohort (mean age 60 yr; 61% women) who subsequently underwent a follow-up exam including an oral glucose tolerance test after a median follow-up time of 16 yr. Logistic regression was used to adjust for covariates.
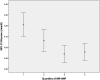
Results: During follow-up, 301 subjects developed new-onset diabetes. After full multivariate adjustment, MR-ANP was significantly inversely associated with incident diabetes (OR = 0.85; 95% CI = 0.73-0.99; P = 0.034) but not N-BNP (OR = 0.92; 95% CI = 0.80-1.06; P = 0.262). In fully adjusted linear regression models, the progression of fasting glucose during follow-up was significantly inversely related to baseline levels of MR-ANP (P = 0.004) but not N-BNP (P = 0.129). Quartile analyses revealed that the overall association was mainly accounted for by excess risk of incident diabetes in subjects belonging to the lowest quartile of MR-ANP. After full adjustment, the odds ratio for incident diabetes in the bottom compared with the top quartile of MR-ANP was 1.65 (OR = 1.08-2.51, P = 0.019) and 1.43 (OR = 1.04-1.96, P = 0.027) compared with all other subjects.
Conclusion: Low plasma levels of MR-ANP predict development of future diabetes and glucose progression over time, suggesting a causal role of ANP deficiency in diabetes development.
Figures
References
-
- John SW, Krege JH, Oliver PM, Hagaman JR, Hodgin JB, Pang SC, Flynn TG, Smithies O. 1995. Genetic decreases in atrial natriuretic peptide and salt-sensitive hypertension. Science 267:679–681 - PubMed
-
- Levin ER, Gardner DG, Samson WK. 1998. Natriuretic peptides. N Engl J Med 339:321–328 - PubMed
-
- Newton-Cheh C, Larson MG, Vasan RS, Levy D, Bloch KD, Surti A, Guiducci C, Kathiresan S, Benjamin EJ, Struck J, Morgenthaler NG, Bergmann A, Blankenberg S, Kee F, Nilsson P, Yin X, Peltonen L, Vartiainen E, Salomaa V, Hirschhorn JN, Melander O, Wang TJ. 2009. Association of common variants in NPPA and NPPB with circulating natriuretic peptides and blood pressure. Nat Genet 41:348–353 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dessì-Fulgheri P, Sarzani R, Tamburrini P, Moraca A, Espinosa E, Cola G, Giantomassi L, Rappelli A. 1997. Plasma atrial natriuretic peptide and natriuretic peptide receptor gene expression in adipose tissue of normotensive and hypertensive obese patients. J Hypertens 15:1695–1699 - PubMed
-
- Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, Benjamin EJ, Leip EP, Wilson PW, Vasan RS. 2004. Impact of obesity on plasma natriuretic peptide levels. Circulation 109:594–600 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical