Specificity protein, Sp1-mediated increased expression of Prdx6 as a curcumin-induced antioxidant defense in lens epithelial cells against oxidative stress
- PMID: 22113199
- PMCID: PMC3223701
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2011.121
Specificity protein, Sp1-mediated increased expression of Prdx6 as a curcumin-induced antioxidant defense in lens epithelial cells against oxidative stress
Abstract
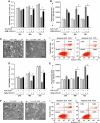
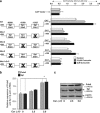
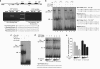
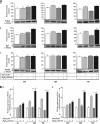
Peroxiredoxin 6 (Prdx6) is a pleiotropic oxidative stress-response protein that defends cells against reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced damage. Curcumin, a naturally occurring agent, has diversified beneficial roles including cytoprotection. Using human lens epithelial cells (hLECs) and Prdx6-deficient cells, we show the evidence that curcumin protects cells by upregulating Prdx6 transcription via invoking specificity protein 1 (Sp1) activity against proapoptotic stimuli. Curcumin enhanced Sp1 and Prdx6 mRNA and protein expression in a concentration-dependent manner, as evidenced by western and real-time PCR analyses, and thereby negatively regulated ROS-mediated apoptosis by blunting ROS expression and lipid peroxidation. Bioinformatic analysis and DNA-protein binding assays disclosed three active Sp1 sites (-19/27, -61/69 and -82/89) in Prdx6 promoter. Co-transfection experiments with Sp1 and Prdx6 promoter-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) constructs showed that CAT activity was dramatically increased in LECs or Sp1-deficient cells (SL2). Curcumin treatment of LECs enhanced Sp1 binding to its sites, consistent with curcumin-dependent stimulation of Prdx6 promoter with Sp1 sites and cytoprotection. Notably, disruption of Sp1 sites by point mutagenesis abolished curcumin transactivation of Prdx6. Also, curcumin failed to activate Prdx6 expression in the presence of Sp1 inhibitors, demonstrating that curcumin-mediated increased expression of Prdx6 was dependent on Sp1 activity. Collectively, the study may provide a foundation for developing transcription-based inductive therapy to reinforce endogenous antioxidant defense by using dietary supplements.
Figures

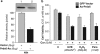


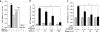
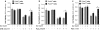
Similar articles
-
Peroxiredoxin 6 in Stress Orchestration and Disease Interplay.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Mar 23;14(4):379. doi: 10.3390/antiox14040379. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40298631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sumoylation-deficient Prdx6 repairs aberrant Sumoylation-mediated Sp1 dysregulation-dependent Prdx6 repression and cell injury in aging and oxidative stress.Aging (Albany NY). 2018 Sep 12;10(9):2284-2315. doi: 10.18632/aging.101547. Aging (Albany NY). 2018. PMID: 30215601 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgolic Acid Rescues Lens Epithelial Cells from Injury Caused by Redox Regulated-Aberrant Sumoylation Signaling by Reviving Prdx6 and Sp1 Expression and Activities.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 8;19(11):3520. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113520. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30413111 Free PMC article.
-
Sp1-mediated upregulation of Prdx6 expression prevents podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy via mitigation of oxidative stress and ferroptosis.Life Sci. 2021 Aug 1;278:119529. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119529. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33894270
-
Anti-Oxidant and Pro-Oxidant Effects of Peroxiredoxin 6: A Potential Target in Respiratory Diseases.Cells. 2023 Jan 1;12(1):181. doi: 10.3390/cells12010181. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36611974 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Peroxiredoxin 6 in Stress Orchestration and Disease Interplay.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Mar 23;14(4):379. doi: 10.3390/antiox14040379. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40298631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction and Collaboration of SP1, HIF-1, and MYC in Regulating the Expression of Cancer-Related Genes to Further Enhance Anticancer Drug Development.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Nov 17;45(11):9262-9283. doi: 10.3390/cimb45110580. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37998757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic analysis in pterygium; upregulated protein expression of ALDH3A1, PDIA3, and PRDX2.Mol Vis. 2014 Aug 27;20:1192-202. eCollection 2014. Mol Vis. 2014. PMID: 25221425 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered Sumoylation-Deficient Prdx6 Mutant Protein-Loaded Nanoparticles Provide Increased Cellular Defense and Prevent Lens Opacity.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Aug 4;10(8):1245. doi: 10.3390/antiox10081245. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439493 Free PMC article.
-
Obligatory Role of AMPK Activation and Antioxidant Defense Pathway in the Regulatory Effects of Metformin on Cellular Protection and Prevention of Lens Opacity.Cells. 2022 Sep 27;11(19):3021. doi: 10.3390/cells11193021. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36230981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balasubramanian D. Ultraviolet radiation and cataract. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2000;16:285–297. - PubMed
-
- Kubo E, Fatma N, Akagi Y, Beier DR, Singh SP, Singh DP. TAT-mediated PRDX6 protein transduction protects against eye lens epithelial cell death and delays lens opacity. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008;294:C842–C855. - PubMed
-
- Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M, Telser J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39:44–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

