MCS9.7 enhancer activity is highly, but not completely, associated with expression of Irf6 and p63
- PMID: 22113860
- PMCID: PMC4936416
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.22786
MCS9.7 enhancer activity is highly, but not completely, associated with expression of Irf6 and p63
Abstract
Background: DNA variation in Interferon Regulatory Factor 6 (IRF6) contributes risk for orofacial clefting, including a common DNA variant rs642961. This DNA variant is located in a multi-species conserved sequence that is 9.7 kb upstream from the IRF6 transcriptional start site (MCS9.7). The MCS9.7 element was shown to possess enhancer activity that mimicked the expression of endogenous Irf6 at embryonic day 11.5 in transient transgenic embryos, and also contains a p63 binding site that transactivates IRF6 expression. To analyze whether the MCS9.7 enhancer is sufficient to drive IRF6 expression, we generated stable transgenic murine lines that carry a MCS9.7-lacZ transgene. We hypothesized that MCS9.7 was sufficient to recapitulate the endogenous expression of Irf6 at other time-points during embryonic development.
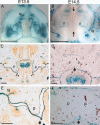
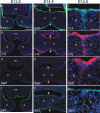
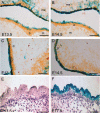
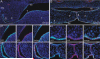
Results: We observed that MCS9.7 activity recapitulated endogenous Irf6 expression in most tissues, but not in the medial edge epithelium (MEE) at E14.5, when Irf6 expression was high during secondary palatal fusion. Also, while MCS9.7 activity and Irf6 expression were associated with p63 expression, we observed MCS9.7 activity and Irf6 expression in periderm, although p63 was absent.
Conclusion: These data suggest that MCS9.7 enhancer activity is not sufficient to recapitulate IRF6 expression, and that p63 expression is not always necessary nor sufficient for transactivation of IRF6.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Bailey CM, Khalkhali-Ellis Z, Kondo S, Margaryan NV, Seftor RE, Wheaton WW, Amir S, Pins MR, Schutte BC, Hendrix MJ. Mammary serine protease inhibitor (Maspin) binds directly to interferon regulatory factor 6: identification of a novel serpin partnership. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:34210–34217. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beaty TH, Murray JC, Marazita ML, Munger RG, Ruczinski I, Hetmanski JB, Liang KY, Wu T, Murray T, Fallin MD, Redett RA, Raymond G, Schwender H, Jin SC, Cooper ME, Dunnwald M, Mansilla MA, Leslie E, Bullard S, Lidral AC, Moreno LM, Menezes R, Vieira AR, Petrin A, Wilcox AJ, Lie RT, Jabs EW, Wu-Chou YH, Chen PK, Wang H, Ye X, Huang S, Yeow V, Chong SS, Jee SH, Shi B, Christensen K, Melbye M, Doheny KF, Pugh EW, Ling H, Castilla EE, Czeizel AE, Ma L, Field LL, Brody L, Pangilinan F, Mills JL, Molloy AM, Kirke PN, Scott JM, Arcos-Burgos M, Scott AF. A genome-wide association study of cleft lip with and without cleft palate identifies risk variants near MAFB and ABCA4. Nat Genet. 2010;42:525–529. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birnbaum S, Ludwig KU, Reutter H, Herms S, de Assis NA, Diaz-Lacava A, Barth S, Lauster C, Schmidt G, Scheer M, Saffar M, Martini M, Reich RH, Schiefke F, Hemprich A, Potzsch S, Potzsch B, Wienker TF, Hoffmann P, Knapp M, Kramer FJ, Nothen MM, Mangold E. IRF6 gene variants in Central European patients with nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate. Eur J Oral Sci. 2009;117:766–769. - PubMed
-
- Burdick AB, Bixler D, Puckett CL. Genetic analysis in families with van der Woude syndrome. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol. 1985;5:181–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

