Calcium/calmodulin kinase II in the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus modulates the initiation and maintenance of wakefulness
- PMID: 22114270
- PMCID: PMC3229030
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3981-11.2011
Calcium/calmodulin kinase II in the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus modulates the initiation and maintenance of wakefulness
Abstract
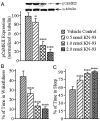
The pedunculopontine tegmentum nucleus (PPT) is critically involved in the regulation of wakefulness (W) and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, but our understanding of the mechanisms of this regulation remains incomplete. The present study was designed to determine the role of PPT intracellular calcium/calmodulin kinase (CaMKII) signaling in the regulation of W and sleep. To achieve this aim, three different concentrations (0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 nmol) of the CaMKII activation inhibitor, KN-93, were microinjected bilaterally (100 nl/site) into the PPT of freely moving rats, and the effects on W, slow-wave sleep (SWS), REM sleep, and levels of phosphorylated CaMKII (pCaMKII) expression in the PPT were quantified. These effects, which were concentration-dependent and affected wake-sleep variables for 3 h, resulted in decreased W, due to reductions in the number and duration of W episodes; increased SWS and REM sleep, due to increases in episode duration; and decreased levels of pCaMKII expression in the PPT. Regression analyses revealed that PPT levels of pCaMKII were positively related with the total percentage of time spent in W (R(2) = 0.864; n = 28 rats; p < 0.001) and negatively related with the total percentage of time spent in sleep (R(2) = 0.863; p < 0.001). These data provide the first direct evidence that activation of intracellular CaMKII signaling in the PPT promotes W and suppresses sleep. These findings are relevant for designing a drug that could treat excessive sleepiness by promoting alertness.
Figures




References
-
- Capece ML, Lydic R. cAMP and protein kinase A modulate cholinergic rapid eye movement sleep generation. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:R1430–R1440. - PubMed
-
- Choi SS, Seo YJ, Shim EJ, Kwon MS, Lee JY, Ham YO, Suh HW. Involvement of phosphorylated Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated protein in the mouse formalin pain model. Brain Res. 2006;1108:28–38. - PubMed
-
- Clements JR, Grant S. Glutamate-like immunoreactivity in neurons of the laterodorsal tegmental and pedunculopontine nuclei in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1990;120:70–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
