Viral single-strand DNA induces p53-dependent apoptosis in human embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 22114676
- PMCID: PMC3219675
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027520
Viral single-strand DNA induces p53-dependent apoptosis in human embryonic stem cells
Abstract
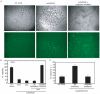
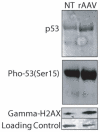
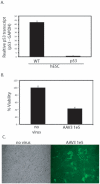
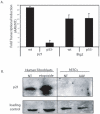
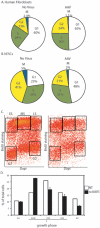
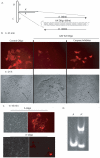
Human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) are primed for rapid apoptosis following mild forms of genotoxic stress. A natural form of such cellular stress occurs in response to recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) single-strand DNA genomes, which exploit the host DNA damage response for replication and genome persistence. Herein, we discovered a unique DNA damage response induced by rAAV transduction specific to pluripotent hESCs. Within hours following rAAV transduction, host DNA damage signaling was elicited as measured by increased gamma-H2AX, ser15-p53 phosphorylation, and subsequent p53-dependent transcriptional activation. Nucleotide incorporation assays demonstrated that rAAV transduced cells accumulated in early S-phase followed by the induction of apoptosis. This lethal signaling sequalae required p53 in a manner independent of transcriptional induction of Puma, Bax and Bcl-2 and was not evident in cells differentiated towards a neural lineage. Consistent with a lethal DNA damage response induced upon rAAV transduction of hESCs, empty AAV protein capsids demonstrated no toxicity. In contrast, DNA microinjections demonstrated that the minimal AAV origin of replication and, in particular, a 40 nucleotide G-rich tetrad repeat sequence, was sufficient for hESC apoptosis. Our data support a model in which rAAV transduction of hESCs induces a p53-dependent lethal response that is elicited by a telomeric sequence within the AAV origin of replication.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Dravid G, Ye Z, Hammond H, Chen G, Pyle A, et al. Defining the role of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in the survival, proliferation, and self-renewal of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2005;10:1489–501. - PubMed
-
- Qin H, Yu T, Qing T, Liu Y, Zhao Y, et al. Regulation of apoptosis and differentiation by p53 in human embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem. 2007;8:5842–52. - PubMed
-
- Grandela C, Pera MF, Wolvetang EJ. p53 is required for etoposide-induced apoptosis of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2007;2:116–28. - PubMed
-
- Raj K, Ogston P, Beard P. Virus-mediated killing of cells that lack p53 activity. Nature. 2001;412:914–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

