Regulatory T cells and IL-10 independently counterregulate cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses induced by transcutaneous immunization
- PMID: 22114725
- PMCID: PMC3218067
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027911
Regulatory T cells and IL-10 independently counterregulate cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses induced by transcutaneous immunization
Abstract
Background: The imidazoquinoline derivate imiquimod induces inflammatory responses and protection against transplanted tumors when applied to the skin in combination with a cognate peptide epitope (transcutaneous immunization, TCI). Here we investigated the role of regulatory T cells (T(reg)) and the suppressive cytokine IL-10 in restricting TCI-induced cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses.
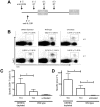
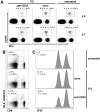
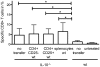
Methodology/principal findings: TCI was performed with an ointment containing the TLR7 agonist imiquimod and a CTL epitope was applied to the depilated back skin of C57BL/6 mice. Using specific antibodies and FoxP3-diphteria toxin receptor transgenic (DEREG) mice, we interrogated inhibiting factors after TCI: by depleting FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells we found that specific CTL-responses were greatly enhanced. Beyond this, in IL-10 deficient (IL-10(-/-)) mice or after blocking of IL-10 signalling with an IL-10 receptor specific antibody, the TCI induced CTL response is greatly enhanced indicating an important role for this cytokine in TCI. However, by transfer of T(reg) in IL-10(-/-) mice and the use of B cell deficient JHT(-/-) mice, we can exclude T(reg) and B cells as source of IL-10 in the setting of TCI.
Conclusion/significance: We identify T(reg) and IL-10 as two important and independently acting suppressors of CTL-responses induced by transcutaneous immunization. Advanced vaccination strategies inhibiting T(reg) function and IL-10 release may lead the development of effective vaccination protocols aiming at the induction of T cell responses suitable for the prophylaxis or treatment of persistent infections or tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Partidos CD, Beignon A-S, Briand J-P, Muller S. Modulation of immune responses with transcutaneously deliverable adjuvants. Vaccine. 2004;22:2385–2390. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2003.11.063. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hemmi H, Kaisho T, Takeuchi O, Sato S, Sanjo H, et al. Small anti-viral compounds activate immune cells via the TLR7 MyD88-dependent signaling pathway. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:196–200. doi: 10.1038/ni758. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sidky YA, Borden EC, Weeks CE, Reiter MJ, Hatcher JF, et al. Inhibition of murine tumor growth by an interferon-inducing imidazoquinolinamine. Cancer Res. 1992;52:3528–3533. - PubMed
-
- Gibson SJ, Imbertson LM, Wagner TL, Testerman TL, Reiter MJ, et al. Cellular requirements for cytokine production in response to the immunomodulators imiquimod and S-27609. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1995;15:537–545. - PubMed
-
- Reiter MJ, Testerman TL, Miller RL, Weeks CE, Tomai MA. Cytokine induction in mice by the immunomodulator imiquimod. J Leukoc Biol. 1994;55:234–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

