Simultaneously typing nine serotypes of enteroviruses associated with hand, foot, and mouth disease by a GeXP analyzer-based multiplex reverse transcription-PCR assay
- PMID: 22116146
- PMCID: PMC3264198
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.05828-11
Simultaneously typing nine serotypes of enteroviruses associated with hand, foot, and mouth disease by a GeXP analyzer-based multiplex reverse transcription-PCR assay
Abstract
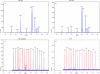
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a contagious enteroviral disease occurring primarily in young children and caused by enterovirus 71 (EV71), coxsackievirus A16 (CVA16), and other serotypes of coxsackievirus and echovirus. In this study, a GeXP analyzer-based multiplex reverse transcription (RT)-PCR assay (GeXP assay) consisting of chimeric primer-based PCR amplification with fluorescent labeling and capillary electrophoresis separation was developed to simultaneously identify nine serotypes of enteroviruses associated with HFMD in China, including EV71, CVA16, CVA4, -5, -9, and -10, and CVB1, -3, and -5. The RNAs extracted from cell cultures of viral isolates and synthetic RNAs via in vitro transcription were used to analyze the specificity and sensitivity of the assay. The GeXP assay detected as little as 0.03 tissue culture infective dose (TCID(50)) of EV71 and CVA16, 10 copies of panenterovirus, EV71, CVA16, CVB1, and CVB5, and 100 copies of 10 (including panenterovirus) premixed RNA templates. A total of 180 stool specimens collected from HFMD patients and persons suspected of having HFMD were used to evaluate the clinical performance of this assay. In comparison with the results of conventional methods, the sensitivities of the GeXP assay for detection of panenterovirus, EV71, and CVA16 were 98.79% (163/165), 91.67% (44/48), and 91.67% (33/36), respectively, and the specificities were 80.00% (12/15), 98.48% (130/132), and 100% (144/144), respectively. The concordance of typing seven other serotypes of enteroviruses with the results of conventional methods was 92.59% (25/27). In conclusion, the GeXP assay is a rapid, cost-effective, and high-throughput method for typing nine serotypes of HFMD-associated enteroviruses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Etiology of Multiple Non-EV71 and Non-CVA16 Enteroviruses Associated with Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease in Jinan, China, 2009-June 2013.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 12;10(11):e0142733. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142733. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26562154 Free PMC article.
-
[Development of a GeXP based multiplex RT-PCR assay for simultaneous differentiation of nine human hand food mouth disease pathogens].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2011 Jul;27(4):331-6. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 21874901 Chinese.
-
[Pathogenic spectrum of enteroviruses associated with hand, foot and mouth disease by a GeXP™-based multiplex reverse transcription-PCR assay in Jinan, China, 2009-2012].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2014 Sep;30(5):567-71. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2014. PMID: 25562968 Chinese.
-
Virus Shedding in Patients With Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease Induced by EV71, CA16 or CA6: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2021 Apr 1;40(4):289-294. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002985. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2021. PMID: 33181780
-
[Prevalence and Analyses of the Changing Etiology of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease in China].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2015 Sep;31(5):554-9. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26738295 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Molecular Characterization of Vibrio cholerae Isolated From Clinical Samples in Kurdistan Province, Iran.Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2015 May 31;8(5):e18119. doi: 10.5812/jjm.8(5)2015.18119. eCollection 2015 May. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26060565 Free PMC article.
-
A novel multiplex tetra-primer ARMS-PCR for the simultaneous genotyping of six single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with female cancers.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 17;8(4):e62126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062126. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23614025 Free PMC article.
-
Charging YOYO-1 on capillary wall for online DNA intercalation and integrating this approach with multiplex PCR and bare narrow capillary-hydrodynamic chromatography for online DNA analysis.Anal Chem. 2015 Feb 3;87(3):1518-22. doi: 10.1021/ac504257b. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25555111 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous detection of eight avian influenza A virus subtypes by multiplex reverse transcription-PCR using a GeXP analyser.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 18;8(1):6183. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24620-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29670227 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Epidemiology Survey of Staphylococcus aureus Panton-Valentine Leukocidin-positive Isolated from Sanandaj, Iran.Adv Biomed Res. 2017 Jul 25;6:87. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_243_15. eCollection 2017. Adv Biomed Res. 2017. PMID: 28828338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abubakar S, Chee HY, Shafee N, Chua KB, Lam SK. 1999. Molecular detection of enteroviruses from an outbreak of hand, foot and mouth disease in Malaysia in 1997. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 31:331–335 - PubMed
-
- Apisarnthanarak A, Kitphati R, Pongsuwann Y, Tacharoenmueng R, Mundy LM. 2005. Echovirus type 11: outbreak of hand-foot-and-mouth disease in a Thai hospital nursery. Clin. Infect. Dis. 41:1361–1362 - PubMed
-
- Barriere H, Berger M, Billaudel S. 1976. Hand, foot and mouth disease. Sem. Hop. 52:2215–2220 [In French.] - PubMed
-
- Bell EJ, McCartney RA, Basquill D, Chaudhuri AK. 1986. Mu-antibody capture ELISA for the rapid diagnosis of enterovirus infections in patients with aseptic meningitis. J. Med. Virol. 19:213–217 - PubMed
-
- Blomqvist S, Klemola P, Kaijalainen S, Paananen A, Simonen ML, Vuorinen T, Roivainen M. 2010. Co-circulation of coxsackieviruses A6 and A10 in hand, foot and mouth disease outbreak in Finland. J. Clin. Virol. 48:49–54 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

