The Creating an Optimal Warfarin Nomogram (CROWN) Study
- PMID: 22116191
- PMCID: PMC4133142
- DOI: 10.1160/TH11-08-0568
The Creating an Optimal Warfarin Nomogram (CROWN) Study
Abstract
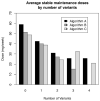
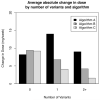
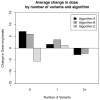
A significant proportion of warfarin dose variability is explained by variation in the genotypes of the cytochrome P450 CYP2C9 and the vitamin K epoxide reductase complex, VKORC1, enzymes that influence warfarin metabolism and sensitivity, respectively. We sought to develop an optimal pharmacogenetic warfarin dosing algorithm that incorporated clinical and genetic information. We enroled patients initiating warfarin therapy. Genotyping was performed of the VKORC1, -1639G>A, the CYP2C9*2, 430C>T, and the CYP2C9*3, 1075C>A genotypes. The initial warfarin dosing algorithm (Algorithm A) was based upon established clinical practice and published warfarin pharmacogenetic information. Subsequent dosing algorithms (Algorithms B and Algorithm C) were derived from pharmacokinetic / pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) modelling of warfarin dose, international normalised ratio (INR), clinical and genetic factors from patients treated by the preceding algorithm(s). The primary outcome was the time in the therapeutic range, considered an INR of 1.8 to 3.2. A total of 344 subjects are included in the study analyses. The mean percentage time within the therapeutic range for each subject increased progressively from Algorithm A to Algorithm C from 58.9 (22.0), to 59.7 (23.0), to 65.8 (16.9) percent (p = 0.04). Improvement also occurred in most secondary endpoints, which included the per-patient percentage of INRs outside of the therapeutic range (p = 0.004), the time to the first therapeutic INR (p = 0.07), and the time to achieve stable therapeutic anticoagulation (p < 0.001). In conclusion, warfarin pharmacogenetic dosing can be optimised in real time utilising observed PK/PD information in an adaptive fashion.
Figures
References
-
- Gallagher AM, Setakis E, Plumb JM, et al. Risks of stroke and mortality associated with subuptimal anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation patients. Thromb Haemost. 2011;106:968–977. - PubMed
-
- Gage BF, Eby C, Milligan PE, et al. Use of pharmacogenetics and clinical factors to predict the mainenance dose of warfarin. Thromb Haemost. 2004;91:87–94. - PubMed

