Fabrication of immunosensor microwell arrays from gold compact discs for detection of cancer biomarker proteins
- PMID: 22116194
- PMCID: PMC3328855
- DOI: 10.1039/c1lc20833k
Fabrication of immunosensor microwell arrays from gold compact discs for detection of cancer biomarker proteins
Abstract
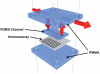
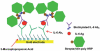
A simple method is reported to fabricate gold arrays featuring microwells surrounding 8-electrodes from gold compact discs (CDs) for less than $0.2 per chip. Integration of these disposable gold CD array chips with microfluidics provided inexpensive immunoarrays that were used to measure a cancer biomarker protein quickly at high sensitivity. The gold CD sensor arrays were fabricated using thermal transfer of laserjet toner from a computer-printed pattern followed by selective chemical etching. Sensor elements had an electrochemically addressable surface area of 0.42 mm(2) with RSD <2%. For a proof-of-concept application, the arrays were integrated into a simple microfluidic device for electrochemical detection of cancer biomarker interleukin-6 (IL-6) in diluted serum. Capture antibodies of IL-6 were chemically linked onto the electrode arrays and a sandwich immunoassay protocol was developed. A biotinylated detection antibody with polymerized horseradish peroxidase labels was used for signal amplification. The detection limit of IL-6 in diluted serum was remarkably low at 10 fg mL(-1) (385 aM) with a linear response with log of IL-6 concentration from 10 to 1300 fg mL(-1). These easily fabricated, ultrasensitive, microfluidic immunosensors should be readily adapted for sensitive detection of multiple biomarkers for cancer diagnostics.
Figures


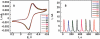
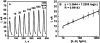

Similar articles
-
Inkjet-printed gold nanoparticle electrochemical arrays on plastic. Application to immunodetection of a cancer biomarker protein.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2011 Mar 21;13(11):4888-94. doi: 10.1039/c0cp01755h. Epub 2011 Jan 7. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2011. PMID: 21212889 Free PMC article.
-
Disposable inkjet-printed electrochemical platform for detection of clinically relevant HER-2 breast cancer biomarker.Biosens Bioelectron. 2018 May 1;104:158-162. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.01.003. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018. PMID: 29331430 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic electrochemical immunoarray for ultrasensitive detection of two cancer biomarker proteins in serum.Biosens Bioelectron. 2011 Jul 15;26(11):4477-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2011.05.005. Epub 2011 May 11. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011. PMID: 21632234 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasensitive immunosensor for cancer biomarker proteins using gold nanoparticle film electrodes and multienzyme-particle amplification.ACS Nano. 2009 Mar 24;3(3):585-94. doi: 10.1021/nn800863w. ACS Nano. 2009. PMID: 19216571 Free PMC article.
-
Printed Electrodes in Microfluidic Arrays for Cancer Biomarker Protein Detection.Biosensors (Basel). 2020 Sep 7;10(9):115. doi: 10.3390/bios10090115. Biosensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32906644 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-Response Duplexing of Electrochemical Label-Free Biosensor from the Same Tag.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Apr;13(11):e2303509. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202303509. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 38245830 Free PMC article.
-
A microfluidic electrochemiluminescent device for detecting cancer biomarker proteins.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013 Apr;405(11):3831-8. doi: 10.1007/s00216-012-6656-5. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013. PMID: 23307128 Free PMC article.
-
Macroporous hydrogel micropillars for quantifying Met kinase activity in cancer cell lysates.Analyst. 2012 Sep 7;137(17):4052-61. doi: 10.1039/c2an35464k. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Analyst. 2012. PMID: 22814332 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid Nanobioengineered Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Biosensors.Molecules. 2022 Jun 15;27(12):3841. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123841. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35744967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrochemiluminescent Array to Detect Oxidative Damage in ds-DNA Using [Os(bpy)2(phen-benz-COOH)]2+/Nafion/Graphene Films.ACS Sens. 2016;1(3):272-278. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.5b00189. Epub 2016 Jan 8. ACS Sens. 2016. PMID: 27135053 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

