Regulatory T cells increase in breast cancer and in stage IV breast cancer
- PMID: 22116346
- PMCID: PMC11029076
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-011-1158-4
Regulatory T cells increase in breast cancer and in stage IV breast cancer
Abstract
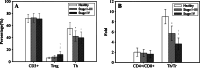
Expression levels of VEGF and Her-2, levels of T-regulatory (Treg) cells, levels of CD3+ cells, and ratios of Th (CD4+ T cells)/Tr (Treg) cells were compared between stage I, II, III, and IV breast cancer patients (n = 120) prior to chemotherapy and healthy women (n = 30). Cells from peripheral blood were counted by flow cytometry, Her-2 and VEGF expression was detected by pathological examination, and Her-2 was detected by FISH. Breast cancer patients had more Treg cells and a lower ratio of Th/Tr cells than the healthy women. Stage IV breast cancer patients had more Treg cells and a lower ratio of Th/Tr cells than stage I, II, or III breast cancer patients. Patients positive for VEGF had a lower ratio of Th/Tr cells compared with patients negative for VEGF, and those positive for both VEGF and Her-2 also had a lower ratio of Th/Tr cells compared with patients not positive for both VEGF and Her-2. The decreased Th/Tr cells ratio indicates impaired immune function, suggesting that the stage IV breast cancer and the Her-2/VEGF-positive breast cancer patients have lower immune function.
Figures
References
-
- Croci DO, Zacarías Fluck MF, Rico MJ, Matar P, Rabinovich GA, Scharovsky OG. Dynamic cross-talk between tumor and immune cells in orchestrating the immunosuppressive network at the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2007;56(11):1687–1700. doi: 10.1007/s00262-007-0343-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abo-Elenein A, Elgohary S, Hashish A, El-Halaby E. Significance of immunoregulatory T cells in different stages of breast cancer patients. Egyptian J Immunol/Egyptian Ass Immunologists. 2008;15(2):145. - PubMed
-
- Sutmuller RP, van Duivenvoorde LM, van Elsas A, Schumacher TN, Wildenberg ME, Allison JP, Toes RE, Offringa R, Melief CJ. Synergism of cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 blockade and depletion of CD25(+) regulatory T cells in antitumor therapy reveals alternative pathways for suppression of autoreactive cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses. J Exp Med. 2001;194(6):823–832. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.6.823. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

