Pitx2 confers left morphological, molecular, and functional identity to the sinus venosus myocardium
- PMID: 22116619
- PMCID: PMC3258653
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvr314
Pitx2 confers left morphological, molecular, and functional identity to the sinus venosus myocardium
Abstract
Aims: The sinus venous myocardium, comprising the sinoatrial node (SAN) and sinus horns (SH), is a region subject to congenital malformations and cardiac arrhythmias. It differentiates from symmetric bilateral mesenchymal precursors, but morphological, molecular, and functional left/right differences are progressively established through development. The role of the laterality gene Pitx2 in this process is unknown. We aimed to elucidate the molecular events driving left/right patterning in the sinus venosus (SV) myocardium by using a myocardial Pitx2 knockout mouse.
Methods and results: We generated a myocardial specific Pitx2 knockout model (cTP mice). cTP embryos present several features of Pitx2 null, including right atrial isomerism with bilateral SANs and symmetric atrial entrance of the systemic veins. By in situ hybridization and optical mapping analysis, we compared throughout development the molecular and functional properties of the SV myocardium in wt and mutant embryos. We observed that Pitx2 prevents the expansion of the left-SAN primordium at the onset of its differentiation into myocardium; Pitx2 promotes expansion of the left SH through development; Pitx2 dose-dependently represses the autorhythmic properties of the left SV myocardium at mid-gestation (E14.5); Pitx2 modulates late foetal gene expression at the left SH-derived superior caval vein.
Conclusion: Pitx2 drives left/right patterning of the SV myocardium through multiple developmental steps. Overall, Pitx2 plays a crucial functional role by negatively modulating a nodal-type programme in the left SV myocardium.
Figures





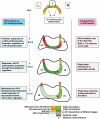
References
-
- Christoffels VM, Mommersteeg MT, Trowe MO, Prall OW, de Gier-de Vries C, Soufan AT, et al. Formation of the venous pole of the heart from an Nkx2-5-negative precursor population requires Tbx18. Circ Res. 2006;98:1555–1563. - PubMed
-
- Sizarov A, Anderson RH, Christoffels VM, Moorman AF. Three-dimensional and molecular analysis of the venous pole of the developing human heart. Circulation. 2010;122:798–807. - PubMed
-
- Attenhofer Jost CH, Connolly HM, Danielson GK, Bailey KR, Schaff HV, Shen WK, et al. Sinus venosus atrial septal defect: long-term postoperative outcome for 115 patients. Circulation. 2005;112:1953–1958. - PubMed
-
- Lin WS, Tai CT, Hsieh MH, Tsai CF, Lin YK, Tsao HM, et al. Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation initiated by non-pulmonary vein ectopy. Circulation. 2003;107:3176–3183. - PubMed
-
- Katritsis DG, Giazitzoglou E, Korovesis S, Karvouni E, Anagnostopoulos CE, Camm AJ. Conduction patterns in the cardiac veins: electrophysiologic characteristics of the connections between left atrial and coronary sinus musculature. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2004;10:51–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

