Memory CD4 T cells induce selective expression of IL-27 in CD8+ dendritic cells and regulate homeostatic naive T cell proliferation
- PMID: 22116827
- PMCID: PMC3244513
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101908
Memory CD4 T cells induce selective expression of IL-27 in CD8+ dendritic cells and regulate homeostatic naive T cell proliferation
Abstract
Naive T cells undergo robust proliferation in lymphopenic conditions, whereas they remain quiescent in steady-state conditions. However, a mechanism by which naive T cells are kept from proliferating under steady-state conditions remains unclear. In this study, we report that memory CD4 T cells are able to limit naive T cell proliferation within lymphopenic hosts by modulating stimulatory functions of dendritic cells (DC). The inhibition was mediated by IL-27, which was primarily expressed in CD8(+) DC subsets as the result of memory CD4 T cell-DC interaction. IL-27 appeared to be the major mediator of inhibition, as naive T cells deficient in IL-27R were resistant to memory CD4 T cell-mediated inhibition. Finally, IL-27-mediated regulation of T cell proliferation was also observed in steady-state conditions as well as during Ag-mediated immune responses. We propose a new model for maintaining peripheral T cell homeostasis via memory CD4 T cells and CD8(+) DC-derived IL-27 in vivo.
Figures
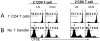





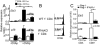

References
-
- Boyman O, Letourneau S, Krieg C, Sprent J. Homeostatic proliferation and survival of naive and memory T cells. Eur J Immunol. 2009;39:2088–2094. - PubMed
-
- Tanchot C, Rosado MM, Agenes F, Freitas AA, Rocha B. Lymphocyte homeostasis. Semin Immunol. 1997;9:331–337. - PubMed
-
- Kieper WC, Troy A, Burghardt JT, Ramsey C, Lee JY, Jiang HQ, Dummer W, Shen H, Cebra JJ, Surh CD. Recent immune status determines the source of antigens that drive homeostatic T cell expansion. J Immunol. 2005;174:3158–3163. - PubMed
-
- Prlic M, Jameson SC. Homeostatic expansion versus antigen-driven proliferation: common ends by different means? Microbes Infect. 2002;4:531–537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

