Highly stable meso-diaminopimelate dehydrogenase from an Ureibacillus thermosphaericus strain A1 isolated from a Japanese compost: purification, characterization and sequencing
- PMID: 22117688
- PMCID: PMC3293039
- DOI: 10.1186/2191-0855-1-43
Highly stable meso-diaminopimelate dehydrogenase from an Ureibacillus thermosphaericus strain A1 isolated from a Japanese compost: purification, characterization and sequencing
Abstract
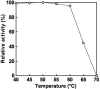
We screened various thermophiles for meso-diaminopimelate dehydrogenase (meso-DAPDH, EC 1.4.1.16), which catalyzes the NAD(P)-dependent oxidative deamination of meso-diaminopimelate, and found the enzyme in a thermophilic bacterium isolated from compost in Japan. The bacterium grew well aerobically at around 55°C and was identified as Ureibacillus thermosphaericus strain A1. We purified the enzyme about 47-fold to homogeneity from crude cell extract using five successive purification steps. The molecular mass of the purified protein was about 80 kDa, and the molecule consists of a homodimer with the subunit molecular mass of about 40 kDa. The optimum pH and temperature for the catalytic activity of the enzyme are about 10.5 and 65°C, respectively. The enzyme is highly selective for meso-diaminopimelate as the electron donor, and NADP but not NAD can serve as the electron acceptor. The Km values for meso-diaminopimelate and NADP at 50°C and pH 10.5 are 1.6 mM and 0.13 mM, respectively. The nucleotide sequence of this meso-DAPDH gene encodes a 326-amino acid peptide. When the gene was cloned and overexpressed in Escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3), the specific activity in the crude extract of the recombinant cells was about 18.0-fold higher than in the extract from U. thermosphaericus strain A1. This made more rapid and simpler purification of the enzyme possible.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Artificial Thermostable D-Amino Acid Dehydrogenase: Creation and Application.Front Microbiol. 2018 Aug 3;9:1760. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01760. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30123202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and functional characterization of NAD(P)+ -dependent meso-diaminopimelate dehydrogenase from Numidum massiliense.Microbiologyopen. 2020 Aug;9(8):e1059. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1059. Epub 2020 Jun 2. Microbiologyopen. 2020. PMID: 32485072 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of an NAD(P)+-dependent meso-diaminopimelate dehydrogenase from Thermosyntropha lipolytica.Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2020 Oct;1868(10):140476. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2020.140476. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2020. PMID: 32599299
-
Structural insight into the thermostable NADP(+)-dependent meso-diaminopimelate dehydrogenase from Ureibacillus thermosphaericus.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2015 May;71(Pt 5):1136-46. doi: 10.1107/S1399004715003673. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2015. PMID: 25945579
-
Creation of a thermostable NADP⁺-dependent D-amino acid dehydrogenase from Ureibacillus thermosphaericus strain A1 meso-diaminopimelate dehydrogenase by site-directed mutagenesis.Biotechnol Lett. 2012 Sep;34(9):1693-9. doi: 10.1007/s10529-012-0952-1. Epub 2012 May 22. Biotechnol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22618239
Cited by
-
Engineered Biocatalysts for the Asymmetric Synthesis of d-Phenylalanines.ACS Catal. 2025 Apr 18;15(9):7361-7389. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5c00837. eCollection 2025 May 2. ACS Catal. 2025. PMID: 40337374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of thermostable meso-diaminopimelate dehydrogenase to redirect diaminopimelate pathway for increasing L-lysine production in Escherichia coli.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 20;9(1):2423. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37974-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30787467 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Sequence of the Thermophilic Soil Bacterium Ureibacillus terrenus ATCC BAA-384T.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2021 Dec 2;10(48):e0105421. doi: 10.1128/MRA.01054-21. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2021. PMID: 34854732 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Cofactor Preference of Thermostable StDAPDH by a Single Mutation at K159.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 5;21(5):1788. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051788. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32150965 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Thermostable D-Amino Acid Dehydrogenase: Creation and Application.Front Microbiol. 2018 Aug 3;9:1760. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01760. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30123202 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Davis BJ. Disc electrophoresis - II method and application to human. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964;121:404–427. - PubMed
-
- Fortina MG, Pukall R, Schumann P, Mora D, Parini C, Manachini PL, Stackebrandt E. Ureibacillus gen. nov., a new genus to accomodate Bacillus thermosphaericus (Andersson et al. 1995), emendation of Ureibacillus thermosphaericus and description of Ureibacillus terrenus sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001;51:447–455. - PubMed
-
- Hudson AO, Klartag A, Gilvarg C, Dobson RC, Marques FG, Leustek T. Dual diaminopimelate biosynthesis pathways in Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium thermocellum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1814:1162–1168. - PubMed
-
- Ishino S, Mizukami T, Yamaguchi K, Katsumata R, Araki K. Cloning and sequencing of the meso-diaminopimelate-D-dehydrogenase (ddh) gene of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Agric Biol Chem. 1988;52:2903–2909. doi: 10.1271/bbb1961.52.2903. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

