Abnormal MDMX degradation in tumor cells due to ARF deficiency
- PMID: 22120712
- PMCID: PMC3290737
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.534
Abnormal MDMX degradation in tumor cells due to ARF deficiency
Abstract
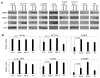
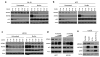
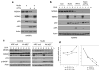
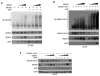
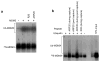
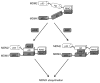
MDMX is a heterodimeric partner of MDM2 and a critical regulator of p53. The MDMX level is generally elevated in tumors with wild-type p53 and contributes to p53 inactivation. MDMX degradation is controlled in part by MDM2-mediated ubiquitination. Here, we show that MDMX turnover is highly responsive to changes in MDM2 level in non-transformed cells, but not in tumor cells. We found that loss of alternate reading frame (ARF) expression, which occurs in most tumors with wild-type p53, significantly reduces MDMX sensitivity to MDM2. Restoration of ARF expression in tumor cells enables MDM2 to degrade MDMX in a dose-dependent manner. ARF binds to MDM2 and stimulates a second-site interaction between the central region of MDM2 and MDMX, and thus increases MDMX-MDM2 binding and MDMX ubiquitination. These results reveal an important abnormality in the p53-regulatory pathway as a consequence of ARF deficiency. Loss of ARF during tumor development not only prevents p53 stabilization by proliferative stress but also causes accumulation of MDMX that compromises p53 activity. This phenomenon may reduce the clinical efficacy of MDM2-specific inhibitors by preventing MDMX downregulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


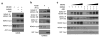

References
-
- Badciong JC, Haas AL. MdmX is a RING finger ubiquitin ligase capable of synergistically enhancing Mdm2 ubiquitination. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:49668–49675. - PubMed
-
- Bothner B, Lewis WS, DiGiammarino EL, Weber JD, Bothner SJ, Kriwacki RW. Defining the molecular basis of Arf and Hdm2 interactions. J Mol Biol. 2001;314:263–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

