Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factors: diverse roles in liver diseases
- PMID: 22120903
- PMCID: PMC3417333
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.25497
Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factors: diverse roles in liver diseases
Abstract
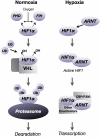
Hypoxia has been shown to have a role in the pathogenesis of several forms of liver disease. The hypoxia inducible factors (HIFs) are a family of evolutionarily conserved transcriptional regulators that affect a homeostatic response to low oxygen tension and have been identified as key mediators of angiogenesis, inflammation, and metabolism. In this review we summarize the evidence for a role of HIFs across a range of hepatic pathophysiology. We describe regulation of the HIFs and review investigations that demonstrate a role for HIFs in the development of liver fibrosis, activation of innate immune pathways, hepatocellular carcinoma, as well as other liver diseases in both human disease as well as murine models.
Copyright © 2011 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Jungermann K, Kietzmann T. Oxygen: modulator of metabolic zonation and disease of the liver. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2000;31:255–260. - PubMed
-
- Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI, Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ, Kriegsheim A, et al. Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science. 2001;292:468–472. - PubMed
-
- Dimova EY, Kietzmann T. Hypoxia-inducible factors: post-translational crosstalk of signaling pathways. Methods Mol Biol. 647:215–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
