Golimumab in combination with methotrexate in Japanese patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: results of the GO-FORTH study
- PMID: 22121129
- PMCID: PMC3372319
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2011.200317
Golimumab in combination with methotrexate in Japanese patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: results of the GO-FORTH study
Abstract
Objective: To assess the efficacy and safety of golimumab + methotrexate (MTX) in Japanese patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: 269 Japanese patients with active RA despite treatment with MTX were randomised (1:1:1) to placebo + MTX (Group 1), golimumab 50 mg + MTX (Group 2) or golimumab 100 mg + MTX (Group 3). Subcutaneous golimumab/placebo was injected every 4 weeks; stable doses of oral MTX (6-8 mg/week) were continued. Patients were allowed to enter early escape (Group 1 added golimumab 50 mg, Group 2 increased golimumab to 100 mg, Group 3 continued golimumab 100 mg) based on swollen/tender joint counts at week 14. The primary study endpoint was achievement of at least 20% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology (ACR20) response criteria at week 14. To control for multiplicity of testing, treatment group comparisons were first made between combined Groups 2 and 3 versus Group 1, followed by comparisons of Group 2 and Group 3 versus Group 1.
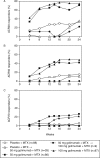
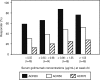
Results: The proportion of patients with an ACR20 response at week 14 was significantly higher in combined Groups 2 and 3 (73.4%, 127/173) and in each of Group 2 (72.1%, 62/86) and Group 3 (74.7%, 65/87) compared with Group 1 (27.3%, 24/88; p<0.0001 for all comparisons). Golimumab + MTX also elicited a significantly better response than placebo + MTX in other efficacy parameters, including disease activity score (DAS28) response/remission and radiographic assessments. During the 16-week fixed treatment regimen study period, 72.7%, 75.6% and 78.2% of patients had adverse events and 1.1%, 1.2% and 2.3% had serious adverse events in Groups 1, 2 and 3, respectively.
Conclusion: In Japanese patients with active RA despite MTX therapy, golimumab + MTX was significantly more effective than MTX monotherapy in reducing RA signs/symptoms and limiting radiographic progression with no unexpected safety concerns.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00727987.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Herman S, Krönke G, Schett G. Molecular mechanisms of inflammatory bone damage: emerging targets for therapy. Trends Mol Med 2008;14:245–53 - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Koeller M, et al. New therapies for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2007;370:1861–74 - PubMed
-
- Emery P, Fleischmann RM, Moreland LW, et al. Golimumab, a human anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody, injected subcutaneously every four weeks in methotrexate-naive patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: twenty-four-week results of a phase III, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of golimumab before methotrexate as first-line therapy for early-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2009;60:2272–83 - PubMed

