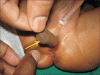
Accessory scrotum in the perineum
- PMID: 22121322
- PMCID: PMC3221166
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-9261.86887
Accessory scrotum in the perineum
Abstract
A case of accessory scrotum in a 2-day-old male infant is reported because of its rarity. An overview of sequences during the normal development of male external genitalia has been provided and the deranged mechanism resulting in this anomaly has been reviewed with hypotheses regarding etiology of accessory scrotum.
Keywords: Anti Mullerian hormone; genital folds; genital swellings.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Luigi A. Genital anomalies. 2008. [Last accessed on 2010 Oct 17]. Available from: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1016681-overview .
-
- Harada M, Udagawa A, Yoshimoto S, Ichinose M. A case of accessory scrotum with perineal lipoma. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2009;62:e108–9. - PubMed
-
- Kolandaivelu G, Seeniraj K, Bose JC, Rajagopal P. Accessory scrotum. Br J Urol. 1987;59:363. - PubMed
-
- Sule JD, Skoog SJ, Tank ES. Perineal lipoma and the accessory labioscrotal fold: An etiologic relationship. J Urol. 1994;151:475–7. - PubMed
-
- Kendirci M, Horasanli K, Miroglu C. Accessory scrotum with multiple skeletal abnormalities. Int J Urol. 2006;13:648–50. - PubMed