Multifunctional iron platinum stealth immunomicelles: targeted detection of human prostate cancer cells using both fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 22121333
- PMCID: PMC3223933
- DOI: 10.1007/s11051-011-0439-3
Multifunctional iron platinum stealth immunomicelles: targeted detection of human prostate cancer cells using both fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
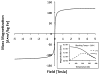
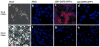
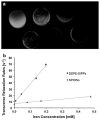
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) are the most common type of contrast agents used in contrast agent-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Still, there is a great deal of room for improvement, and nanoparticles with increased MRI relaxivities are needed to increase the contrast enhancement in MRI applied to various medical conditions including cancer. We report the synthesis of superparamagnetic iron platinum nanoparticles (SIPPs) and subsequent encapsulation using PEGylated phospholipids to create stealth immunomicelles (DSPE-SIPPs) that can be specifically targeted to human prostate cancer cell lines and detected using both MRI and fluorescence imaging. SIPP cores and DSPE-SIPPs were 8.5 ± 1.6 nm and 42.9 ± 8.2 nm in diameter, respectively, and the SIPPs had a magnetic moment of 120 A m(2)/kg iron. J591, a monoclonal antibody against prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA), was conjugated to the DSPE-SIPPs (J591-DSPE-SIPPs), and specific targeting of J591-DSPE-SIPPs to PSMA-expressing human prostate cancer cell lines was demonstrated using fluorescence confocal microscopy. The transverse relaxivity of the DSPE-SIPPs, measured at 4.7 Tesla, was 300.6 ± 8.5 s(-1) mM(-1), which is 13-fold better than commercially available SPIONs (23.8 ± 6.9 s(-1) mM(-1)) and ~3-fold better than reported relaxivities for Feridex(®) and Resovist(®). Our data suggest that J591-DSPE-SIPPs specifically target human prostate cancer cells in vitro, are superior contrast agents in T(2)-weighted MRI, and can be detected using fluorescence imaging. To our knowledge, this is the first report on the synthesis of multifunctional SIPP micelles and using SIPPs for the specific detection of prostate cancer.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Paclitaxel-loaded iron platinum stealth immunomicelles are potent MRI imaging agents that prevent prostate cancer growth in a PSMA-dependent manner.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:4341-52. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S34381. Epub 2012 Aug 6. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22915856 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and magnetic characterization of superparamagnetic iron platinum nanoparticle contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging.J Vac Sci Technol B Nanotechnol Microelectron. 2012 Mar;30(2):02C101. doi: 10.1116/1.3692250. Epub 2012 Mar 5. J Vac Sci Technol B Nanotechnol Microelectron. 2012. PMID: 25317380 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of carbon chain length on the synthesis and yield of fatty amine-coated iron-platinum nanoparticles.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2014 Jun 17;9(1):306. doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-9-306. eCollection 2014. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2014. PMID: 25006334 Free PMC article.
-
Quenched indocyanine green-anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen antibody J591.2011 Dec 8 [updated 2012 Mar 1]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2011 Dec 8 [updated 2012 Mar 1]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 22400137 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Quantum dot 800–prostate-specific membrane antigen antibody J591.2011 Feb 28 [updated 2011 May 18]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2011 Feb 28 [updated 2011 May 18]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 21634075 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative [Fe]MRI determination of the dynamics of PSMA-targeted SPIONs discriminates among prostate tumor xenografts based on their PSMA expression.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018 Aug;48(2):469-481. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25935. Epub 2018 Jan 13. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29331081 Free PMC article.
-
Low-toxicity FePt nanoparticles for the targeted and enhanced diagnosis of breast tumors using few centimeters deep whole-body photoacoustic imaging.Photoacoustics. 2020 Apr 11;19:100179. doi: 10.1016/j.pacs.2020.100179. eCollection 2020 Sep. Photoacoustics. 2020. PMID: 32322488 Free PMC article.
-
Area-Selective Atomic Layer Deposition of Metal Oxides on Noble Metals through Catalytic Oxygen Activation.Chem Mater. 2018 Feb 13;30(3):663-670. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b03818. Epub 2017 Dec 1. Chem Mater. 2018. PMID: 29503508 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of prostate cancer cells using flexible fluorescent polymers.Anal Chem. 2012 Jan 3;84(1):17-20. doi: 10.1021/ac202301k. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Anal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22148518 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal monitoring of microglial/macrophage activation in ischemic rat brain using Iba-1-specific nanoparticle-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020 Dec;40(1_suppl):S117-S133. doi: 10.1177/0271678X20953913. Epub 2020 Sep 22. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020. PMID: 32960690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrew W, Wender RC, Etzioni RB, Thompson IM, D’Amico AV, Volk RJ, Brooks DD, Dash C, Guessous I, Andrews K, DeSantis C, Smith RA. American cancer society guideline for the early detection of prostate cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60(2):70–98. - PubMed
-
- Barmak K, Kim J, Lewis LH, Coffey KR, Toney MF, Kellock AJ, Thiele JU. Stoichiometry: anisotropy connections in epitaxial L10 FePt(001) films. Paper presented at the Magnetism and Magnetic Materials Conference; Anaheim, CA, USA. 2004.
-
- Basit L, Nepijko SA, Shukoor I, Ksenofontov V, Klimenkov M, Fecher GH, Schonhense G, Tremel W, Felser C. Structure and magnetic properties of iron–platinum particles with y-ferric-oxide shell. Appl Phys A. 2009;94:619–625.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
