Is there a regulatory role of immunoglobulins on tissue forming cells relevant in chronic inflammatory lung diseases?
- PMID: 22121383
- PMCID: PMC3216316
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/721517
Is there a regulatory role of immunoglobulins on tissue forming cells relevant in chronic inflammatory lung diseases?
Abstract
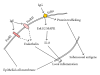
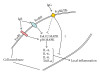
Epithelial cells, fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells together form and give structure to the airway wall. These three tissue forming cell types are structure giving elements and participate in the immune response to inhaled particles including allergens and dust. All three cell types actively contribute to the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory lung diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Tissue forming cells respond directly to allergens through activated immunoglobulins which then bind to their corresponding cell surface receptors. It was only recently reported that allergens and particles traffic through epithelial cells without modification and bind to the immunoglobulin receptors on the surface of sub-epithelial mesenchymal cells. In consequence, these cells secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby extending the local inflammation. Furthermore, activation of the immunoglobulin receptors can induce proliferation and tissue remodeling of the tissue forming cells. New studies using anti-IgE antibody therapy indicate that the inhibition of immunoglobulins reduces the response of tissue forming cells. The unmeasured questions are: (i) why do tissue forming cells express immunoglobulin receptors and (ii) do tissue forming cells process immunoglobulin receptor bound particles? The focus of this review is to provide an overview of the expression and function of various immunoglobulin receptors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Airway smooth muscle cells respond directly to inhaled environmental factors.Swiss Med Wkly. 2010 Aug 27;140:w13066. doi: 10.4414/smw.2010.13066. eCollection 2010. Swiss Med Wkly. 2010. PMID: 20458646 Review.
-
Muscarinic receptors on airway mesenchymal cells: novel findings for an ancient target.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Feb;26(1):145-55. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2012.07.003. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 22842340 Review.
-
Contributions of IL-33 in Non-hematopoietic Lung Cells to Obstructive Lung Disease.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 13;11:1798. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01798. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32903501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate immune responses to environmental allergens.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2006 Apr;30(2):129-40. doi: 10.1385/criai:30:2:129. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16645224 Review.
-
Methods for Experimental Allergen Immunotherapy: Subcutaneous and Sublingual Desensitization in Mouse Models of Allergic Asthma.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2223:295-335. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1001-5_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33226602
References
-
- Reddel HK, Lim TK, Mishima M, Wainwright CE, Knight DA. Year-in-review 2010: asthma, COPD, cystic fibrosis and airway biology. Respirology. 2011;16(3):540–552. - PubMed
-
- Hariri LP, Mino-Kenudson M, Shea B, et al. Distinct histopathology of acute onset or abrupt exacerbation of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Human Pathology. In press. - PubMed
-
- Cox LA., Jr. An exposure-response threshold for lung diseases and lung cancer caused by crystalline silica. Risk Analysis. 2011;31(10):1543–1560. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

