[Primary malignant tumors of the small intestine: clinical and therapeutic aspects of 27 patients]
- PMID: 22121427
- PMCID: PMC3201583
[Primary malignant tumors of the small intestine: clinical and therapeutic aspects of 27 patients]
Abstract
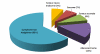
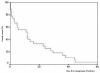
Les tumeurs malignes de l’intestin grêle (TMPIG) sont des tumeurs rares. Elles représentent 1 à 5% de toutes les tumeurs du tube digestif. Elles sont caractérisées par une hétérogénéité anatomopathologique et une symptomatologie pauvre et non spécifique entrainant ainsi un retard diagnostic, des difficultés Thérapeutiques et donc un mauvais pronostic. Nous rapportant les caractéristiques épidémiologiques, diagnostiques et thérapeutiques ainsi que la survie des patients atteints des TMIG au sein de l’institut national d’oncologie de Rabat. Il s’agit d’une analyse rétrospective des dossiers cliniques des 27 patients ayant le diagnostic de tumeurs malignes de l’intestin grêle admis dans notre institut entre 1998 et 2002. L’âge médian était de 46 ans (15-70 ans). Le délai médian de diagnostic était de 6 mois (0-96 mois). La douleur abdominale était le symptôme le plus fréquent (77.8%). L’étude anatomopathologique a montré 63% de lymphome non Hodgkinien, 14.8% d’adénocarcinome, 7.4% de tumeur stromale, 7.4% de carcinome neuroendocrine et 7.4% de sarcome intestinal. Vingt patients (76. 9%) ont eu une résection chirurgicale et 14 patients (53. 8%) ont eu une chimiothérapie en fonction du stade de la maladie et du type histologique. Après un recul médian de 11.6 mois, la survie globale après 12 mois était de 44.4% et la médiane de survie était de 11.6 mois. Les tumeurs malignes de l’intestin grêle sont rares. Leur diagnostic est tardif limitant ainsi la prise en charge thérapeutique curative. Les cliniciens doivent être avertis des symptômes gastro-intestinaux non spécifiques.
Figures
References
-
- Tissot E, Berger F, Valette PJ, Ayoun CL, German J. Malignant tumors of the small intestine. Rev Prat. 1985;21;35(41):2495, 2501–2498, 2504. - PubMed
-
- Adler SN, Lyon DT, Sullivan PD. Adenocarcinoma of the small bowel: Clinical features, similarity to regional enteritis, and analysis of 338 documented cases. Am J Gastroenterol. 1982;77(5):326–330. - PubMed
-
- Herbsman H, Wetstein L, Rosen Y, Orces H, Alfonso AE, Iyer SK. et al. Tumors of the small intestine. Curr Probl Surg. 1980;17(3):121–182. - PubMed
-
- Martin RG. Malignant tumors of the small intestine. Surg Clin North Am. 1986;66:779–785. - PubMed
-
- Hatzaras I, Palesty JA, Abir F, Sullivan P, Kozol RA, Dudrick SJ, Longo WE. Small-bowel tumors: epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of 1260 cases from the connecticut tumor registry. Arch Surg. 2007;235;142:229. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
