Gastrointestinal stromal tumor causing ileo-ileal intussusception in an adult patient a rare presentation with review of literature
- PMID: 22121438
- PMCID: PMC3201593
- DOI: 10.4314/pamj.v8i1.71086
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor causing ileo-ileal intussusception in an adult patient a rare presentation with review of literature
Abstract
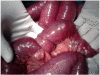
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) are mesenchymal tumors occurring anywhere along the gastrointestinal tract and are believed to originate from the interstitial cells of Cajal. They commonly arise in the stomach or small intestine. The usual growth pattern is exophytic invading adjacent organs or perforation into the peritoneal cavity which may result in bleeding or obstructive symptoms. Intussusception and obstruction is a very uncommon presentation of these lesions because of their tendency to grow in an extraluminal fashion. We report an unusual case of 59 yrs old man presenting with acute small bowel obstruction, which on exploration was found to be due to ileo-ileal intussusception and the lead point of intussusception was a tumor, which was histologically diagnosed as GIST.
Keywords: Acute small bowel obstruction; Gastrointestinal stromal tumor; Ileo-ileal intussusception.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ileoileal intussusception induced by a gastrointestinal stromal tumor.World J Surg Oncol. 2008 Dec 17;6:133. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-6-133. World J Surg Oncol. 2008. PMID: 19091094 Free PMC article.
-
[Gastroduodenal intussusception due to pedunculated polypoid gastrointestinal stromal tumor].Korean J Gastroenterol. 2012 May;59(5):372-6. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2012.59.5.372. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22617532 Korean.
-
Ileocolic intussusception due to a gastrointestinal stromal tumor.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2012 Feb;23(1):87-8. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22505390 No abstract available.
-
Neonatal Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor of the Sigmoid Colon: A Case Report and Review of Literature.Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2020 Apr;39(2):172-178. doi: 10.1080/15513815.2019.1641861. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31329002 Review.
-
Myoepithelial hamartoma causing small-bowel intussusception: a case report and literature review.Pediatr Surg Int. 2006 Apr;22(4):387-9. doi: 10.1007/s00383-005-1616-1. Epub 2006 Jan 26. Pediatr Surg Int. 2006. PMID: 16572349 Review.
Cited by
-
Adult intussusception: a challenge to laparoscopic surgery?PeerJ. 2022 Nov 30;10:e14495. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14495. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36518277 Free PMC article.
-
Community teaching hospital surgical experience with adult intussusception: Study of nine cases and literature review.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;12:26-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2015.03.032. Epub 2015 May 1. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 25989258 Free PMC article.
-
A rare case of jejuno-ileal intussusception secondary to a gastrointestinal stromal tumour.J Surg Case Rep. 2015 Jan 8;2015(1):rju142. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rju142. J Surg Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 25576166 Free PMC article.
-
Jejunojejunal intussusception with chronic bleeding caused by gastrointestinal stromal tumor: a case report and literature review.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Jun;13(3):1481-1488. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-301. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35837170 Free PMC article.
-
Small bowel intussusception in an adult secondary to gastrointestinal stromal tumor: a rare case report.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Apr 7;85(5):1952-1955. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000458. eCollection 2023 May. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37228926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghaderi H, Jafarian A, Aminian A, Daryasari SA. Clinical Presentations, Diagnosis and Treatment of Adult Intussusception, a 20 years survey. Int J Surg. 2010;8(4):318–20. - PubMed
-
- Matheiowetz P, Voigt J, Faller G, Siegel E. Ultrasound diagnosis of intussusception: report of two cases. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2010 Mar;135(12):563–6. Epub 2010 Mar 16. This article on PubMed. - PubMed
-
- Haas EM, Etter EL, Ellis S, Taylor TV. Adult intussusception. Am J Surg. 2003 Jul;186(1):75–6. - PubMed
-
- Paredes MP Guillén, Soto A Campillo, Lorenzo JG Martín, Martínez JA Torralba, Ballester M Mengual, Baldó MJ Cases, Albasini JL Aguayo. Adult intussusception - 14 case reports and their outcomes. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2010 Jan;102(1):32–40. - PubMed
-
- Occhionorelli S, Mitaritonno M, Pennella A, Carella M, Presicce L, Pellegrini D, Fiore MG, Fonte V Pollinzi. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST): case report. G Chir. 2001;22:65–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical