Memory modulation
- PMID: 22122145
- PMCID: PMC3236701
- DOI: 10.1037/a0026187
Memory modulation
Abstract
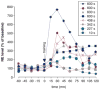
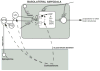
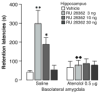
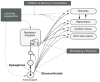
Our memories are not all created equally strong: Some experiences are well remembered while others are remembered poorly, if at all. Research on memory modulation investigates the neurobiological processes and systems that contribute to such differences in the strength of our memories. Extensive evidence from both animal and human research indicates that emotionally significant experiences activate hormonal and brain systems that regulate the consolidation of newly acquired memories. These effects are integrated through noradrenergic activation of the basolateral amygdala that regulates memory consolidation via interactions with many other brain regions involved in consolidating memories of recent experiences. Modulatory systems not only influence neurobiological processes underlying the consolidation of new information, but also affect other mnemonic processes, including memory extinction, memory recall, and working memory. In contrast to their enhancing effects on consolidation, adrenal stress hormones impair memory retrieval and working memory. Such effects, as with memory consolidation, require noradrenergic activation of the basolateral amygdala and interactions with other brain regions.
PsycINFO Database Record (c) 2011 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures



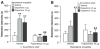


References
-
- Abe K. Modulation of hippocampal long-term potentiation by the amygdala: a synaptic mechanism linking emotion and memory. Japanese Journal of Pharmacology. 2001;86:18–22. - PubMed
-
- Abercrombie HC, Kalin NH, Thurow ME, Rosenkranz MA, Davidson RJ. Cortisol variation in humans affects memory for emotionally laden and neutral information. Behavioral Neuroscience. 2003;117:506–516. - PubMed
-
- Abercrombie HC, Speck NS, Monticelli RM. Endogenous cortisol elevations are related to memory facilitation only in individuals who are emotionally aroused. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2006;31:187–196. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R, Cahill L, Schul R, Babinsky R. Impaired declarative memory for emotional material following bilateral amygdala damage in humans. Learning & Mememory. 1997;4:51–54. - PubMed
-
- Aguilar-Valles A, Sanchez E, de Gortari P, Balderas I, Ramirez-Amaya V, Bermudez-Rattoni F, Joseph-Bravo P. Analysis of the stress response in rats trained in the water-maze: differential expression of corticotropin-releasing hormone, CRH-R1, glucocorticoid receptors and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in limbic regions. Neuroendocrinology. 2005;82:306–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

