Differential brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in limbic brain regions following social defeat or territorial aggression
- PMID: 22122152
- PMCID: PMC3232038
- DOI: 10.1037/a0026172
Differential brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in limbic brain regions following social defeat or territorial aggression
Erratum in
- Behav Neurosci. 2012 Feb;126(1):156
Abstract
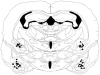
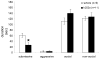
Syrian hamsters readily form dominant-subordinate relationships under laboratory conditions. Winning or losing in agonistic encounters can have striking, long-term effects on social behavior, but the mechanisms underlying this experience-induced behavioral plasticity are unclear. The present study tested the hypothesis that changes in brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) may at least in part mediate this plasticity. Male hamsters were paired for 15-min using a resident-intruder model, and individuals were identified as winners or losers on the basis of their behavior. BDNF was examined with in situ hybridization 2 hr after treatment during the consolidation period of emotional learning. Losing animals had significantly more BDNF mRNA in the basolateral (BLA) and medial (MeA) nuclei of the amygdala when compared with winning animals as well as novel cage and home cage controls. Interestingly, winning animals had significantly more BDNF mRNA in the dentate gyrus of the dorsal hippocampus than did losing animals, novel, and home cage controls. No conflict-related changes in BDNF mRNA were observed in several other regions including the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and central amygdala. Next, we demonstrated that K252a, a Trk receptor antagonist, significantly reduced the acquisition of conditioned defeat when administered within the BLA. These data support a model in which BDNF-mediated plasticity within the BLA supports learning of submission or subordinate social status in losing animals, whereas BDNF-mediated plasticity within the hippocampus may instantiate aspects of winning such as control of a territory in dominant animals.
PsycINFO Database Record (c) 2011 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Arborelius L, Owens MJ, Plotsky PM, Nemeroff CB. The role of corticotropin-releasing factor in depression and anxiety disorders. J Endocrinology. 1999;160:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Berton O, McClung CA, DiLeone RJ, Krishnan V, Renthal W, Russo SJ, Graham D, Tsankova NM, Bolanos CA, Rios M, Monteggia LM, Self DW, Nestler EJ. Essential role of BDNF in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway in social defeat stress. Science. 2006;311:864–868. - PubMed
-
- Bjorkqvist K. Social defeat as a stressor in humans. Physiology and Behav. 2001;73:435–442. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard RJ, Blanchard DC. Antipredator defensive behaviors in a visible burrow system. Journal of Comparative Psychology. 1989;103:70–82. - PubMed

