The CETP I405V polymorphism is associated with an increased risk of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 22122979
- PMCID: PMC3306495
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00777.x
The CETP I405V polymorphism is associated with an increased risk of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
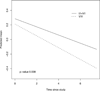
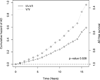
The cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) gene plays an essential role in regulating cholesterol homeostasis and is a candidate susceptibility gene for late-onset Alzheimer's disease (AD). Recent finding suggests that the CETP I405V polymorphism (rs5882) is associated with a slower rate of memory decline and a lower risk of incident dementia. Using data from two ongoing epidemiologic clinical-pathologic cohort studies of aging and dementia in the United States, the Religious Order Study and the Memory and Aging Project, we evaluated the association of the CETP I405V polymorphism (rs5882) with cognitive decline and risk of incident AD in more than 1300 participants of European ancestry. Our results suggest that the CETP I405V polymorphism was associated with a faster rather than a slower rate of decline in cognition over time, and an increased risk of incident AD. This finding is consistent with data showing that the CETP I405V is associated with increased neuritic plaque density at autopsy.
© 2011 The Authors. Aging Cell © 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd/Anatomical Society of Great Britain and Ireland.
Figures
References
-
- Arias-Vasquez A, Isaacs A, Aulchenko YS, Hofman A, Oostra BA, Breteler M, van Duijn CM. The cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) gene and the risk of Alzheimers disease. Neurogenetics. 2007;8:189–193. - PubMed
-
- Barter PJ, Kastelein JJ. Targeting cholesteryl ester transfer protein for the prevention and management of cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47(3):492–499. - PubMed
-
- Bennett DA, Wilson RS, Schneider JA, et al. Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 allele, AD pathology, and the clinical expression of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 2003;60:246–252. - PubMed
-
- Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Buchman AS, et al. The Rush Memory and Aging Project: study design and baseline characteristics of the study cohort. Neuroepidemiology. 2005a;25:163–175. - PubMed
-
- Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Bienias JL, et al. Mild cognitive impairment is related to Alzheimer disease pathology and cerebral infarctions. Neurology. 2005b;64:834–841. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

