Age-dependent changes in the cerebrospinal fluid proteome by slow off-rate modified aptamer array
- PMID: 22122984
- PMCID: PMC3349859
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.10.024
Age-dependent changes in the cerebrospinal fluid proteome by slow off-rate modified aptamer array
Abstract
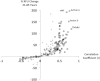
An important precondition for the successful development of diagnostic assays of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers of age-related neurodegenerative diseases is an understanding of the dynamic nature of the CSF proteome during the normal aging process. In this study, a novel proteomic technology was used to quantify hundreds of proteins simultaneously in the CSF from 90 cognitively normal adults 21 to 85 years of age. SomaLogic's highly multiplexed proteomic platform can measure more than 800 proteins simultaneously from small volumes of biological fluids using novel slow off-rate modified aptamer (SOMAmer) protein affinity reagents with sensitivity, specificity, and dynamic ranges that meet or exceed those of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. In the first application of this technology to CSF, we detected 248 proteins that possessed signals greater than twofold over background. Several novel correlations between detected protein concentrations and age were discovered that indicate that both inflammation and response to injury in the central nervous system may increase with age. Applying this powerful proteomic approach to CSF provides potential new insight into the aging of the human central nervous system that may have utility in discovering new disease-related changes in the CSF proteome.
Copyright © 2012 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

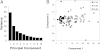
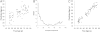
References
-
- Warren J., Schott J., Fox N., Thom M., Revesz T., Holton J., Scaravilli F., Thomas D., Plant G., Rudge P., Rossor M. Brain biopsy in dementia. Brain. 2005;128:2016–2025. - PubMed
-
- Verbeek M., De Jong D., Kremer H. Brain-specific proteins in cerebrospinal fluid for the diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases. Ann Clin Biochem. 2003;40:25–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

