Rational identification of an optimal antibody mixture for targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor
- PMID: 22123060
- PMCID: PMC3242845
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.3.6.17955
Rational identification of an optimal antibody mixture for targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor
Abstract
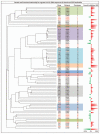
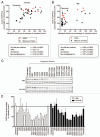
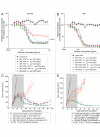
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is frequently dysregulated in human malignancies and a validated target for cancer therapy. Two monoclonal anti-EGFR antibodies (cetuximab and panitumumab) are approved for clinical use. However, the percentage of patients responding to treatment is low and many patients experiencing an initial response eventually relapse. Thus, the need for more efficacious treatments remains. Previous studies have reported that mixtures of antibodies targeting multiple distinct epitopes are more effective than single mAbs at inhibiting growth of human cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. The current work describes the rational approach that led to discovery and selection of a novel anti-EGFR antibody mixture Sym004, which is currently in Phase 2 clinical testing. Twenty-four selected anti-EGFR antibodies were systematically tested in dual and triple mixtures for their ability to inhibit cancer cells in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. The results show that targeting EGFR dependent cancer cells with mixtures of antibodies is superior at inhibiting their growth both in vitro and in vivo. In particular, antibody mixtures targeting non-overlapping epitopes on domain III are efficient and indeed Sym004 is composed of two monoclonal antibodies targeting this domain. The superior growth inhibitory activity of mixtures correlated with their ability to induce efficient EGFR degradation.
Figures


References
-
- Bublil EM, Yarden Y. The EGF receptor family: spearheading a merger of signaling and therapeutics. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19:124–134. - PubMed
-
- Harris RC, Chung E, Coffey RJ. EGF receptor ligands. Exp Cell Res. 2003;284:2–13. - PubMed
-
- Ogiso H, Ishitani R, Nureki O, Fukai S, Yamanaka M, Kim JH, et al. Crystal structure of the complex of human epidermal growth factor and receptor extracellular domains. Cell. 2002;110:775–787. - PubMed
-
- Garrett TP, McKern NM, Lou M, Elleman TC, Adams TE, Lovrecz GO, et al. Crystal structure of a truncated epidermal growth factor receptor extracellular domain bound to transforming growth factor alpha. Cell. 2002;110:763–773. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson KM, Berger MB, Mendrola JM, Cho HS, Leahy DJ, Lemmon MA. EGF activates its receptor by removing interactions that autoinhibit ectodomain dimerization. Mol Cell. 2003;11:507–517. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
