Phytochrome-interacting factor 4 (PIF4) regulates auxin biosynthesis at high temperature
- PMID: 22123947
- PMCID: PMC3250122
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1110682108
Phytochrome-interacting factor 4 (PIF4) regulates auxin biosynthesis at high temperature
Abstract
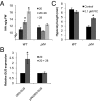
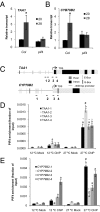
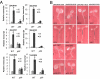
At high ambient temperature, plants display dramatic stem elongation in an adaptive response to heat. This response is mediated by elevated levels of the phytohormone auxin and requires auxin biosynthesis, signaling, and transport pathways. The mechanisms by which higher temperature results in greater auxin accumulation are unknown, however. A basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor, PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR 4 (PIF4), is also required for hypocotyl elongation in response to high temperature. PIF4 also acts redundantly with its homolog, PIF5, to regulate diurnal growth rhythms and elongation responses to the threat of vegetative shade. PIF4 activity is reportedly limited in part by binding to both the basic helix-loop-helix protein LONG HYPOCOTYL IN FAR RED 1 and the DELLA family of growth-repressing proteins. Despite the importance of PIF4 in integrating multiple environmental signals, the mechanisms by which PIF4 controls growth are unknown. Here we demonstrate that PIF4 regulates levels of auxin and the expression of key auxin biosynthesis genes at high temperature. We also identify a family of SMALL AUXIN UP RNA (SAUR) genes that are expressed at high temperature in a PIF4-dependent manner and promote elongation growth. Taken together, our results demonstrate direct molecular links among PIF4, auxin, and elongation growth at high temperature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Vanneste S, Friml J. Auxin: A trigger for change in plant development. Cell. 2009;136:1005–1016. - PubMed
-
- Bartel B. Auxin biosynthesis. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1997;48:51–66. - PubMed
-
- Koini MA, et al. High temperature-mediated adaptations in plant architecture require the bHLH transcription factor PIF4. Curr Biol. 2009;19:408–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 243140/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- BB/D0100470/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- GM067203/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM067203/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- BBS/E/J/00000610/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

