Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II function in vascular remodelling
- PMID: 22124148
- PMCID: PMC3382326
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.222232
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II function in vascular remodelling
Abstract
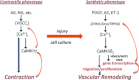
Vascular smooth muscle (VSM) undergoes a phenotypic switch in response to injury, a process that contributes to pathophysiological vascular wall remodelling. VSM phenotype switching is a consequence of changes in gene expression, including an array of ion channels and pumps affecting spatiotemporal features of intracellular Ca(2+) signals. Ca(2+) signalling promotes vascular wall remodelling by regulating cell proliferation, motility, and/or VSM gene transcription, although the mechanisms are not clear. In this review, the functions of multifunctional Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) in VSM phenotype switching and synthetic phenotype function are considered. CaMKII isozymes have complex structural and autoregulatory properties. Vascular injury in vivo results in rapid changes in CaMKII isoform expression with reduced expression of CaMKIIγ and upregulation of CaMKIIδ in medial wall VSM. SiRNA-mediated suppression of CaMKIIδ or gene deletion attenuates VSM proliferation and consequent neointimal formation. In vitro studies support functions for CaMKII in the regulation of cell proliferation, motility and gene expression via phosphorylation of CREB1 and HDACIIa/MEF2 complexes. These studies support the concept, and provide potential mechanisms, whereby Ca(2+) signalling through CaMKIIδ promotes VSM phenotype transitions and vascular remodelling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thymine DNA glycosylase is a key regulator of CaMKIIγ expression and vascular smooth muscle phenotype.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 Nov 1;317(5):H969-H980. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00146.2019. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31518169 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II in Vascular Smooth Muscle.Adv Pharmacol. 2017;78:171-202. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2016.08.003. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Adv Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28212797 Review.
-
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-delta isoform regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007 Jun;292(6):C2276-87. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00606.2006. Epub 2007 Jan 31. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17267544
-
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-γ (CaMKIIγ) negatively regulates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and vascular remodeling.FASEB J. 2016 Mar;30(3):1051-64. doi: 10.1096/fj.15-279158. Epub 2015 Nov 13. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 26567004 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiomyocyte calcium and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: friends or foes?Recent Prog Horm Res. 2004;59:141-68. doi: 10.1210/rp.59.1.141. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2004. PMID: 14749501 Review.
Cited by
-
Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)-stimulated fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation is mediated by hyaluronan (HA)-facilitated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and CD44 co-localization in lipid rafts.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 24;288(21):14824-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.451336. Epub 2013 Apr 15. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23589287 Free PMC article.
-
Thymine DNA glycosylase is a key regulator of CaMKIIγ expression and vascular smooth muscle phenotype.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 Nov 1;317(5):H969-H980. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00146.2019. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31518169 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase 2 mediates Epac-induced spontaneous transient outward currents in rat vascular smooth muscle.J Physiol. 2017 Sep 15;595(18):6147-6164. doi: 10.1113/JP274754. Epub 2017 Aug 14. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28731505 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of Dicer in smooth muscle affects voiding pattern and reduces detrusor contractility and neuroeffector transmission.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35882. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035882. Epub 2012 Apr 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22558254 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Vascular Smooth Muscle Contraction and the Basis for Pharmacologic Treatment of Smooth Muscle Disorders.Pharmacol Rev. 2016 Apr;68(2):476-532. doi: 10.1124/pr.115.010652. Pharmacol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27037223 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abraham ST, Benscoter H, Schworer CM, Singer HA. In situ dependence for activation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in vascular smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:2506–2513. - PubMed
-
- Abraham ST, Benscoter HA, Schworer CM, Singer HA. A role for CaM kinase II in the MAP kinase signaling cascade in cultured rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1997;81:575–584. - PubMed
-
- Backs J, Backs T, Neef S, Kreusser MM, Lehmann LH, Patrick DM, Grueter CE, Qi X, Richardson JA, Hill JA, Katus HA, Bassel-Duby R, Maier LS, Olson EN. The delta isoform of CaM kinase II is required for pathological cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling after pressure overload. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:2342–2347. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

