Endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibits STAT3-dependent suppression of hepatic gluconeogenesis via dephosphorylation and deacetylation
- PMID: 22124464
- PMCID: PMC3237645
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-1684
Endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibits STAT3-dependent suppression of hepatic gluconeogenesis via dephosphorylation and deacetylation
Abstract
In the liver, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) plays an important role in the suppression of gluconeogenic enzyme expression. While obesity-associated endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress has been shown to increase hepatic gluconeogenic enzyme expression, the role of ER stress in STAT3-dependent regulation of such expression is unclear. The current study aimed to elucidate the effect of ER stress on the STAT3-dependent regulation of hepatic gluconeogenic enzyme expression. Genetically obese/diabetic db/db mice and db/db mouse-derived isolated hepatocytes were used as ER stress models. A tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor, a deacetylation inhibitor, and an acetylated mutant of STAT3 were used to examine the effect of ER stress on hepatic STAT3 action. ER stress inhibited STAT3-dependent suppression of gluconeogenic enzyme gene expression by suppressing hepatic Janus kinase (JAK)2 and STAT3 phosphorylation. A tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor restored ER stress-induced suppression of JAK2 phosphorylation but exhibited no improving effect on suppressed STAT3 phosphorylation. STAT3 acetylation is known to correlate with its phosphorylation. ER stress also decreased STAT3 acetylation. An acetylated mutant of STAT3 was resistant to ER stress-induced inhibition of STAT3-phosphorylation and STAT3-dependent suppression of hepatic gluconeogenic enzyme gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, ameliorated ER stress-induced inhibition of STAT3 acetylation and phosphorylation. The current study revealed that ER stress inhibits STAT3-dependent suppression of hepatic gluconeogenic enzymes via JAK2 dephosphorylation and HDAC-dependent STAT3 deacetylation, playing an important role in the increase of hepatic glucose production in obesity and diabetes.
Figures
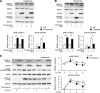

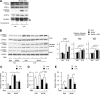
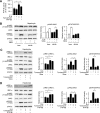
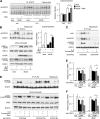



References
-
- Radziuk J, Pye S. Hepatic glucose uptake, gluconeogenesis and the regulation of glycogen synthesis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2001;17:250–272 - PubMed
-
- Herzig S, Long F, Jhala US, et al. CREB regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis through the coactivator PGC-1. Nature 2001;413:179–183 - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto M, Pocai A, Rossetti L, Depinho RA, Accili D. Impaired regulation of hepatic glucose production in mice lacking the forkhead transcription factor Foxo1 in liver. Cell Metab 2007;6:208–216 - PubMed
-
- Dentin R, Liu Y, Koo SH, et al. Insulin modulates gluconeogenesis by inhibition of the coactivator TORC2. Nature 2007;449:366–369 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

