Na(+)-D-glucose cotransporter SGLT1 is pivotal for intestinal glucose absorption and glucose-dependent incretin secretion
- PMID: 22124465
- PMCID: PMC3237647
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-1029
Na(+)-D-glucose cotransporter SGLT1 is pivotal for intestinal glucose absorption and glucose-dependent incretin secretion
Abstract
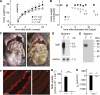
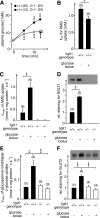
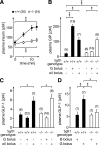
To clarify the physiological role of Na(+)-D-glucose cotransporter SGLT1 in small intestine and kidney, Sglt1(-/-) mice were generated and characterized phenotypically. After gavage of d-glucose, small intestinal glucose absorption across the brush-border membrane (BBM) via SGLT1 and GLUT2 were analyzed. Glucose-induced secretion of insulinotropic hormone (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) in wild-type and Sglt1(-/-) mice were compared. The impact of SGLT1 on renal glucose handling was investigated by micropuncture studies. It was observed that Sglt1(-/-) mice developed a glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome but thrive normally when fed a glucose-galactose-free diet. In wild-type mice, passage of D-glucose across the intestinal BBM was predominantly mediated by SGLT1, independent the glucose load. High glucose concentrations increased the amounts of SGLT1 and GLUT2 in the BBM, and SGLT1 was required for upregulation of GLUT2. SGLT1 was located in luminal membranes of cells immunopositive for GIP and GLP-1, and Sglt1(-/-) mice exhibited reduced glucose-triggered GIP and GLP-1 levels. In the kidney, SGLT1 reabsorbed ∼3% of the filtered glucose under normoglycemic conditions. The data indicate that SGLT1 is 1) pivotal for intestinal mass absorption of d-glucose, 2) triggers the glucose-induced secretion of GIP and GLP-1, and 3) triggers the upregulation of GLUT2.
Figures



Comment in
-
Comment on: Gorboulev et al. Na+-D-glucose cotransporter SGLT1 Is pivotal for intestinal glucose absorption and glucose-dependent incretin secretion. Diabetes 2012;61:187-196.Diabetes. 2012 Jun;61(6):e4; author reply e5. doi: 10.2337/db11-1793. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22618779 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Marsenic O. Glucose control by the kidney: an emerging target in diabetes. Am J Kidney Dis 2009;53:875–883 - PubMed
-
- Brubaker PL. Incretin-based therapies: mimetics versus protease inhibitors. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2007;18:240–245 - PubMed
-
- Wright EM, Loo DDF, Hirayama BA. Biology of human sodium glucose transporters. Physiol Rev 2011;91:733–794 - PubMed
-
- Uldry M, Thorens B. The SLC2 family of facilitated hexose and polyol transporters. Pflugers Arch 2004;447:480–489 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

