Repetitive DNA and next-generation sequencing: computational challenges and solutions
- PMID: 22124482
- PMCID: PMC3324860
- DOI: 10.1038/nrg3117
Repetitive DNA and next-generation sequencing: computational challenges and solutions
Erratum in
- Nat Rev Genet. 2012 Feb;13(2):146
Abstract
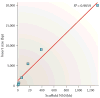
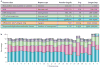
Repetitive DNA sequences are abundant in a broad range of species, from bacteria to mammals, and they cover nearly half of the human genome. Repeats have always presented technical challenges for sequence alignment and assembly programs. Next-generation sequencing projects, with their short read lengths and high data volumes, have made these challenges more difficult. From a computational perspective, repeats create ambiguities in alignment and assembly, which, in turn, can produce biases and errors when interpreting results. Simply ignoring repeats is not an option, as this creates problems of its own and may mean that important biological phenomena are missed. We discuss the computational problems surrounding repeats and describe strategies used by current bioinformatics systems to solve them.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

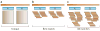

References
-
- Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-seq. Nature Methods. 2008;5:621–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

