Mechanisms of HGF/Met signaling to Brk and Sam68 in breast cancer progression
- PMID: 22124844
- PMCID: PMC3971994
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-011-0097-z
Mechanisms of HGF/Met signaling to Brk and Sam68 in breast cancer progression
Abstract
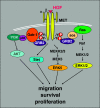
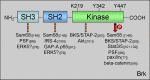
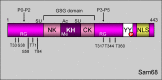
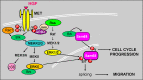
Signal transduction pathways downstream of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are often deregulated during oncogenesis, tumor progression, and metastasis. In particular, the peptide growth factor hormone, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), and its specific receptor, Met tyrosine kinase, regulate cancer cell migration, thereby conferring an aggressive phenotype (Nakamura et al., J Clin Invest 106(12):1511-1519, 2000; Huh et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:4477-4482, 2004). Additionally, overexpression of Met is associated with enhanced invasiveness of breast cancer cells (Edakuni et al., Pathol Int 51(3):172-178, 2001; Jin et al., Cancer 79(4):749-760, 1997; Tuck et al., Am J Pathol 148(1):225-232, 1996). Here, we review the regulation of recently identified novel downstream mediators of HGF/Met signaling, Breast tumor kinase (Brk/PTK6), and Src-associated substrate during mitosis of 68 kDa (Sam68), and discuss their relevance to mechanisms of breast cancer progression.
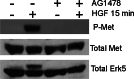
Figures
References
-
- Edakuni G, et al. Expression of the hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met pathway is increased at the cancer front in breast carcinoma. Pathol Int. 2001;51(3):172–178. - PubMed
-
- Jin L, et al. Expression of scatter factor and c-met receptor in benign and malignant breast tissue. Cancer. 1997;79(4):749–760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

