Evidence-based annotation of gene function in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 using genome-wide fitness profiling across 121 conditions
- PMID: 22125499
- PMCID: PMC3219624
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002385
Evidence-based annotation of gene function in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 using genome-wide fitness profiling across 121 conditions
Abstract
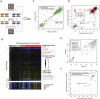
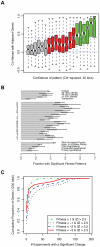
Most genes in bacteria are experimentally uncharacterized and cannot be annotated with a specific function. Given the great diversity of bacteria and the ease of genome sequencing, high-throughput approaches to identify gene function experimentally are needed. Here, we use pools of tagged transposon mutants in the metal-reducing bacterium Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 to probe the mutant fitness of 3,355 genes in 121 diverse conditions including different growth substrates, alternative electron acceptors, stresses, and motility. We find that 2,350 genes have a pattern of fitness that is significantly different from random and 1,230 of these genes (37% of our total assayed genes) have enough signal to show strong biological correlations. We find that genes in all functional categories have phenotypes, including hundreds of hypotheticals, and that potentially redundant genes (over 50% amino acid identity to another gene in the genome) are also likely to have distinct phenotypes. Using fitness patterns, we were able to propose specific molecular functions for 40 genes or operons that lacked specific annotations or had incomplete annotations. In one example, we demonstrate that the previously hypothetical gene SO_3749 encodes a functional acetylornithine deacetylase, thus filling a missing step in S. oneidensis metabolism. Additionally, we demonstrate that the orphan histidine kinase SO_2742 and orphan response regulator SO_2648 form a signal transduction pathway that activates expression of acetyl-CoA synthase and is required for S. oneidensis to grow on acetate as a carbon source. Lastly, we demonstrate that gene expression and mutant fitness are poorly correlated and that mutant fitness generates more confident predictions of gene function than does gene expression. The approach described here can be applied generally to create large-scale gene-phenotype maps for evidence-based annotation of gene function in prokaryotes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






References
-
- Rost B. Enzyme function less conserved than anticipated. J Mol Biol. 2002;318:595–608. - PubMed
-
- Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP. Orthologous transcription factors in bacteria have different functions and regulate different genes. PLoS Comput Biol. 2007;3:e175. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030175. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

