Functions of GSK-3 Signaling in Development of the Nervous System
- PMID: 22125510
- PMCID: PMC3221276
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2011.00044
Functions of GSK-3 Signaling in Development of the Nervous System
Abstract
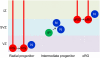
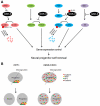
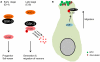
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is central to multiple intracellular pathways including those activated by Wnt/β-catenin, Sonic Hedgehog, Notch, growth factor/RTK, and G protein-coupled receptor signals. All of these signals importantly contribute to neural development. Early attention on GSK-3 signaling in neural development centered on the regulation of neuronal polarity using in vitro paradigms. However, recent creation of appropriate genetic models has demonstrated the importance of GSK-3 to multiple aspects of neural development including neural progenitor self-renewal, neurogenesis, neuronal migration, neural differentiation, and synaptic development.
Keywords: GSK-3; neural progenitor; neuronal migration.
Figures
References
-
- Akhmanova A., Hoogenraad C. C., Drabek K., Stepanova T., Dortland B., Verkerk T., Vermeulen W., Burgering B. M., De Zeeuw C. I., Grosveld F., Galjart N. (2001). Clasps are CLIP-115 and -170 associating proteins involved in the regional regulation of microtubule dynamics in motile fibroblasts. Cell 104, 923–93510.1016/S0092-8674(01)00288-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Araki R., Hoki Y., Uda M., Nakamura M., Jincho Y., Tamura C., Sunayama M., Ando S., Sugiura M., Yoshida M. A., Kasama Y., Abe M. (2011). Crucial role of C-myc in the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 29, 1362–1370 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

