Telmisartan versus valsartan in patients with hypertension: effects on cardiovascular, metabolic, and inflammatory parameters
- PMID: 22125557
- PMCID: PMC3221900
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2011.41.10.583
Telmisartan versus valsartan in patients with hypertension: effects on cardiovascular, metabolic, and inflammatory parameters
Abstract
Background and objectives: Angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) have beneficial effects on cardiovascular, metabolic, and inflammatory parameters in addition to controlling blood pressure (BP). However, few comparative clinical studies have been conducted with different ARBs. We compared these effects in patients with uncomplicated hypertension who were receiving telmisartan or valsartan.
Subjects and methods: The subjects were patients with essential hypertension (48.4±9.6 years) who were randomly assigned to take either telmisartan (80 mg/day, n=30) or valsartan (160 mg/day, n=30) for 12 weeks. Their anthropometric, laboratory, vascular, and echocardiographic data were measured at baseline and at the end of the study.
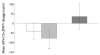
Results: Baseline characteristics were not significantly different between the two groups, except for the carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (cfPWV; telmisartan group vs. valsartan group; 841.2±131.0 vs. 761.1±104.4 cm/s, p<0.05). After 12 weeks, BP had fallen to a similar extent with mean reductions in the systolic and diastolic BP of 20.7±18.1 and 16.3±13.0 mm Hg (p<0.001, respectively) for the telmisartan and 22.5±17.0 and 16.8±9.3 mm Hg (p<0.001, respectively) for the valsartan group. Although the cfPWV and left ventricular mass index (LVMI) fell significantly only with the administration of telmisartan, they were not significantly different when baseline cfPWV was considered. The differences in the cfPWV and LVMI changes from baseline between the two groups were also not significant after adjusting for baseline cfPWV. No significant changes in other vascular, metabolic, or inflammatory parameters were observed with either treatment.
Conclusion: The effects of a 12-week treatment with the two ARBs, telmisartan and valsartan, on cardiovascular, metabolic, and inflammatory parameters were not different in patients with uncomplicated hypertension.
Keywords: Hypertension; Valsartan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
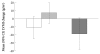
References
-
- Sierra C, de la Sierra A. Antihypertensive, cardiovascular, and pleiotropic effects of angiotensin-receptor blockers. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2005;14:435–441. - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, et al. 2007 guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2007;28:1462–1536. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S, Sleight P, Pogue J, Bosch J, Davies R, Dagenais G. Effects of an angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, on cardiovascular events in high-risk patients: the Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:145–153. - PubMed
-
- Dahlöf B, Devereux RB, Kjeldsen SE, et al. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the Losartan Intervention for Endpoint Reduction in Hypertension Study (LIFE): a randomized trial against atenolol. Lancet. 2002;359:995–1003. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

