Overexpression of Kpnβ1 and Kpnα2 importin proteins in cancer derives from deregulated E2F activity
- PMID: 22125623
- PMCID: PMC3220698
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027723
Overexpression of Kpnβ1 and Kpnα2 importin proteins in cancer derives from deregulated E2F activity
Abstract
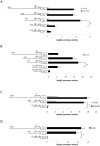
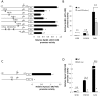
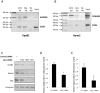
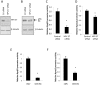
The Karyopherin superfamily comprises nuclear transport proteins, involved in the shuttling of certain cargo proteins into and out of the nucleus. Karyopherin β1 (Kpnβ1) and Karyopherin α2 (Kpnα2) are importin proteins, which work in concert to transport their cargo into the nucleus. We previously identified increased expression of Kpnβ1 and Kpnα2 in cervical tumours compared to normal epithelium and in transformed cells compared to their normal counterparts. This study therefore aimed to identify the transcription regulatory mechanisms associated with high Kpnβ1 and Kpnα2 levels in cancer cells. Kpnβ1 (-2013 to +100) and Kpnα2 (-1900 to +69) promoter fragments were separately cloned into the reporter vector, pGL3-basic, and luciferase assays revealed both as significantly more active in cancer and transformed cells compared to normal. A series of deletion constructs identified the -637 to -271 Kpnβ1 and -180 to -24 Kpnα2 promoter regions as responsible for the differential promoter activity, and a number of highly conserved E2F binding sites were identified within these regions. Mutation analysis confirmed the requirement of E2F sites for promoter activity, and ChIP analysis confirmed E2F2/Dp1 binding to the Kpnβ1 and Kpnα2 promoters in vivo. Dp1 inhibition resulted in decreased levels of the respective proteins, confirming the role of E2F in the overexpression of Kpnβ1 and Kpnα2 proteins in cancer. E2F activity is known to be deregulated in cervical cancer cells due to the inhibition of its repressor, Rb, by HPV E7. The inhibition of E7 using siRNA resulted in decreased Kpnβ1 and Kpnα2 promoter activities, as did the overexpression of Rb. In conclusion, this study is a first to show that elevated Kpnβ1 and Kpnα2 expression in cancer cells correlates with altered transcriptional regulation associated with deregulated E2F/Rb activities.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Karyopherin proteins, Crm1 and Karyopherin beta1, are overexpressed in cervical cancer and are critical for cancer cell survival and proliferation.Int J Cancer. 2009 Apr 15;124(8):1829-40. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24146. Int J Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19117056 Free PMC article.
-
E2F-HDAC complexes negatively regulate the tumor suppressor gene ARHI in breast cancer.Oncogene. 2006 Jan 12;25(2):230-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209025. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16158053
-
A tight balance of Karyopherin β1 expression is required in cervical cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2018 Nov 16;18(1):1123. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5044-8. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30445944 Free PMC article.
-
The nuclear import receptor Kpnβ1 and its potential as an anticancer therapeutic target.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2013;23(1):1-10. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.2013004845. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2013. PMID: 23557333 Review.
-
The role of E2F2 in cancer progression and its value as a therapeutic target.Front Immunol. 2024 May 14;15:1397303. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1397303. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38807594 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Importin-β/karyopherin-β1 modulates mitotic microtubule function and taxane sensitivity in cancer cells via its nucleoporin-binding region.Oncogene. 2020 Jan;39(2):454-468. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-0989-x. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 31492900
-
Investigation of RIP140 and LCoR as independent markers for poor prognosis in cervical cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 31;8(62):105356-105371. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22187. eCollection 2017 Dec 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29285256 Free PMC article.
-
The role of KPNβ1 in neuro-oncology.Onco Targets Ther. 2017 Apr 10;10:2067-2068. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S136247. eCollection 2017. Onco Targets Ther. 2017. PMID: 28435297 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Karyopherin alpha2 is essential for rRNA transcription and protein synthesis in proliferative keratinocytes.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 3;8(10):e76416. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076416. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24098495 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Karyopherin Alpha 2 and Karyopherin Beta 1 Correlate with Poor Prognosis in Gastric Cancer.Oncology. 2022;100(12):685-695. doi: 10.1159/000526807. Epub 2022 Oct 21. Oncology. 2022. PMID: 36273446 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakielny S, Dreyfuss G. Transport of proteins and RNAs in and out of the nucleus. Cell 23; 1999;99(7):677–90. - PubMed
-
- Chook YM, Blobel G. Karyopherins and nuclear import. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001;11(6):703–15. - PubMed
-
- Noetzel E, Rose M, Bornemann J, Gajewski M, Knuchel R, et al. Nuclear transport receptor karyopherin-alpha2 promotes malignant breast cancer phenotypes in vitro. Oncogene. 2011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

