Effects of DPP-4 inhibitors on the heart in a rat model of uremic cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 22125632
- PMCID: PMC3220703
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027861
Effects of DPP-4 inhibitors on the heart in a rat model of uremic cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Background: Uremic cardiomyopathy contributes substantially to mortality in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) may improve cardiac function, but is mainly degraded by dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4).
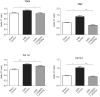
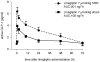
Methodology/principal findings: In a rat model of chronic renal failure, 5/6-nephrectomized [5/6N] rats were treated orally with DPP-4 inhibitors (linagliptin, sitagliptin, alogliptin) or placebo once daily for 4 days from 8 weeks after surgery, to identify the most appropriate treatment for cardiac dysfunction associated with CKD. Linagliptin showed no significant change in blood level AUC(0-∞) in 5/6N rats, but sitagliptin and alogliptin had significantly higher AUC(0-∞) values; 41% and 28% (p = 0.0001 and p = 0.0324), respectively. No correlation of markers of renal tubular and glomerular function with AUC was observed for linagliptin, which required no dose adjustment in uremic rats. Linagliptin 7 µmol/kg caused a 2-fold increase in GLP-1 (AUC 201.0 ng/l*h) in 5/6N rats compared with sham-treated rats (AUC 108.6 ng/l*h) (p = 0.01). The mRNA levels of heart tissue fibrosis markers were all significantly increased in 5/6N vs control rats and reduced/normalized by linagliptin.
Conclusions/significance: DPP-4 inhibition increases plasma GLP-1 levels, particularly in uremia, and reduces expression of cardiac mRNA levels of matrix proteins and B-type natriuretic peptides (BNP). Linagliptin may offer a unique approach for treating uremic cardiomyopathy in CKD patients, with no need for dose-adjustment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitors (gliptins): focus on drug-drug interactions.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2010 Sep;49(9):573-88. doi: 10.2165/11532980-000000000-00000. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2010. PMID: 20690781 Review.
-
Significance of vascular dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition on vascular protection in Zucker diabetic fatty rats.J Pharmacol Sci. 2014;125(4):386-93. doi: 10.1254/jphs.14052fp. Epub 2014 Jul 17. J Pharmacol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25030743
-
The DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin restores β-cell function and survival in human isolated islets through GLP-1 stabilization.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Jul;98(7):E1163-72. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-1029. Epub 2013 Apr 30. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23633194
-
Linagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor in development for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a Phase I, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of single and multiple escalating doses in healthy adult male Japanese subjects.Clin Ther. 2010 Jun;32(6):1188-204. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.06.004. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 20637971 Clinical Trial.
-
An update in incretin-based therapy: a focus on dipeptidyl peptidase--4 inhibitors.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2012 May;8(3):169-82. doi: 10.2174/157339912800564007. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2012. PMID: 22429011 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardioprotective effects of sitagliptin against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016 Aug;241(14):1577-87. doi: 10.1177/1535370216643418. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016. PMID: 27037281 Free PMC article.
-
Abelmoschus esculentus subfractions improved nephropathy with regulating dipeptidyl peptidase-4 and type 1 glucagon-like peptide receptor in type 2 diabetic rats.J Food Drug Anal. 2019 Jan;27(1):135-144. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2018.07.004. Epub 2018 Aug 14. J Food Drug Anal. 2019. PMID: 30648566 Free PMC article.
-
Incretins and selective renal sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in hypertension and coronary heart disease.World J Diabetes. 2015 Sep 10;6(11):1186-97. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i11.1186. World J Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 26380062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of renal dipeptidyl peptidase-4 in kidney disease: renal effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors with a focus on linagliptin.Clin Sci (Lond). 2018 Feb 28;132(4):489-507. doi: 10.1042/CS20180031. Print 2018 Feb 28. Clin Sci (Lond). 2018. PMID: 29491123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linagliptin Ameliorates Methylglyoxal-Induced Peritoneal Fibrosis in Mice.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 11;11(8):e0160993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160993. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27513960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Foley RN, Murray AM, Li S, Herzog CA, McBean AM, et al. Chronic kidney disease and the risk for cardiovascular disease, renal replacement, and death in the United States Medicare population, 1998 to 1999. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:489–495. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1296–1305. - PubMed
-
- Tonelli M, Wiebe N, Culleton B, House A, Rabbat C, et al. Chronic kidney disease and mortality risk: a systematic review. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:2034–2047. - PubMed
-
- Ossum A, van Deurs U, Engstrom T, Jensen JS, Treiman M. The cardioprotective and inotropic components of the postconditioning effects of GLP-1 and GLP-1(9-36)a in an isolated rat heart. Pharmacol Res. 2009;60:411–417. - PubMed
-
- Best JH, Hoogwerf BJ, Herman WH, Pelletier EM, Smith DB, et al. Risk of cardiovascular disease events in patients with type 2 diabetes prescribed the glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist exenatide twice daily or other glucose-lowering therapies: a retrospective analysis of the LifeLink database. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:90–95. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

