Insular volume abnormalities associated with different transition probabilities to psychosis
- PMID: 22126702
- PMCID: PMC3413195
- DOI: 10.1017/S0033291711002716
Insular volume abnormalities associated with different transition probabilities to psychosis
Abstract
Background: Although individuals vulnerable to psychosis show brain volumetric abnormalities, structural alterations underlying different probabilities for later transition are unknown. The present study addresses this issue by means of voxel-based morphometry (VBM).
Method: We investigated grey matter volume (GMV) abnormalities by comparing four neuroleptic-free groups: individuals with first episode of psychosis (FEP) and with at-risk mental state (ARMS), with either long-term (ARMS-LT) or short-term ARMS (ARMS-ST), compared to the healthy control (HC) group. Using three-dimensional (3D) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), we examined 16 FEP, 31 ARMS, clinically followed up for on average 3 months (ARMS-ST, n=18) and 4.5 years (ARMS-LT, n=13), and 19 HC.
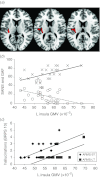
Results: The ARMS-ST group showed less GMV in the right and left insula compared to the ARMS-LT (Cohen's d 1.67) and FEP groups (Cohen's d 1.81) respectively. These GMV differences were correlated positively with global functioning in the whole ARMS group. Insular alterations were associated with negative symptomatology in the whole ARMS group, and also with hallucinations in the ARMS-ST and ARMS-LT subgroups. We found a significant effect of previous antipsychotic medication use on GMV abnormalities in the FEP group.
Conclusions: GMV abnormalities in subjects at high clinical risk for psychosis are associated with negative and positive psychotic symptoms, and global functioning. Alterations in the right insula are associated with a higher risk for transition to psychosis, and thus may be related to different transition probabilities.
Figures

References
-
- Ashburner J. A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage. 2007;38:95. - PubMed
-
- Borgwardt SJ McGuire PK Aston J Berger G Dazzan P Gschwandtner U Pflüger M D'Souza M Radue EW Riecher-Rössler A 2007aStructural brain abnormalities in individuals with an at-risk mental state who later develop psychosis British Journal of Psychiatry. Supplement 51s69–s75. - PubMed
-
- Borgwardt SJ, McGuire PK, Aston J, Gschwandtner U, Pflüger MO, Stieglitz RD, Radue EW, Riecher-Rössler A. Reductions in frontal, temporal and parietal volume associated with the onset of psychosis. Schizophrenia Research. 2008;106:108–114. - PubMed
-
- Borgwardt SJ Riecher-Rössler A Dazzan P Chitnis X Aston J Drewe M Gschwandtner U Haller S Pfluger M Rechsteiner E D'Souza M Stieglitz RD Radue EW McGuire PK 2007bRegional gray matter volume abnormalities in the at risk mental state Biological Psychiatry 611148–1156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

