The nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor signaling network and its role in cancer
- PMID: 22127113
- PMCID: PMC3305885
The nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor signaling network and its role in cancer
Abstract
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a member of the EGFR family of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). EGFR activation via ligand binding results in signaling through various pathways ultimately resulting in cellular proliferation, survival, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. Aberrant expression or activity of EGFR has been strongly linked to the etiology of several human epithelial cancers including but not limited to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), colorectal cancer (CRC), breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, and brain cancer. Thus intense efforts have been made to inhibit the activity of EGFR by designing antibodies against the ligand binding domains (cetuximab and panitumumab) or small molecules against the tyrosine kinase domain (erlotinib, gefitinib, and lapatinib). Although targeting membrane-bound EGFR has shown benefit, a new and emerging role for EGFR is now being elucidated. In this review we will summarize the current knowledge of the nuclear EGFR signaling network, including how it is trafficked to the nucleus, the functions it serves in the nucleus, and how these functions impact cancer progression, survival, and response to chemotherapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflict of interest
Figures
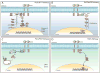
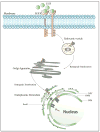
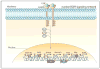
References
-
- Bandyopadhyay D, Mandal M, Adam L, Mendelsohn J, Kumar R. Physical interaction between epidermal growth factor receptor and DNA-dependent protein kinase in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(3):1568–1573. - PubMed
-
- Cao H, Lei ZM, Bian L, Rao CV. Functional nuclear epidermal growth factor receptors in human choriocarcinoma JEG-3 cells and normal human placenta. Endocrinology. 1995;136(7):3163–3172. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter G, King L, Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor stimulates phosphorylation in membrane preparations in vitro. Nature. 1978;276(5686):409–410. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter G, Lembach KJ, Morrison MM, Cohen S. Characterization of the binding of 125-I-labeled epidermal growth factor to human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1975;250(11):4297–4304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

