Age-related loss of noradrenergic neurons in the brains of triple transgenic mice
- PMID: 22127507
- PMCID: PMC3543748
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-011-9343-0
Age-related loss of noradrenergic neurons in the brains of triple transgenic mice
Abstract
Microscopic findings in Alzheimer's disease (AD) at autopsy include a wide cortical distribution of beta amyloid (Aβ)-containing plaques and diminished numbers of pyramidal neurons in CA1 of hippocampus and tyrosine hydroxylase-positive (TH+) neurons in the locus coeruleus (LC). To better understand the neuropathology underlying cognitive decline in AD, we analyzed the AD-type neuropathology in brains of triple transgenic (3×Tg) mice harboring mutations for APP(swe), PS1(M146V), and tau(P301L). Histochemical and immunohistochemical staining and computerized stereology were carried out in age-matched young, early middle age, and late middle age 3×Tg mice. The 3×Tg mice showed an intracellular Aβ deposition in subiculum and CA1 pyramidal neurons and an extracellular distribution of amyloid plaques specifically in the subiculum of hippocampal formation and in neocortical layer V. The 3×Tg mice also showed an age-related loss of TH+ neurons in LC, with a loss of 37% of these neurons at 15 months of age. There was no loss of CA1 neurons at any age examined. Reduced AD-type neuropathology in CA1 of 3×Tg mice suggests a possible neuroprotective role for high intracellular-to-extracellular ratios of insoluble Aβ deposits. Understanding the neurobiology of this apparent neuroprotection could lead to an improved understanding of age-related cognitive function in general, and the development of novel strategies for the therapeutic management of AD patients.
Figures
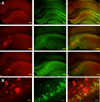
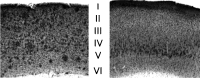
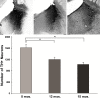
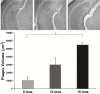
Similar articles
-
Catecholaminergic neuronal loss in locus coeruleus of aged female dtg APP/PS1 mice.J Chem Neuroanat. 2007 Nov;34(3-4):102-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2007.05.008. Epub 2007 May 31. J Chem Neuroanat. 2007. PMID: 17658239 Free PMC article.
-
Widespread Reduced Density of Noradrenergic Locus Coeruleus Axons in the App Knock-In Mouse Model of Amyloid-β Amyloidosis.J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;82(4):1513-1530. doi: 10.3233/JAD-210385. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 34180416 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropathology of mice carrying mutant APP(swe) and/or PS1(M146L) transgenes: alterations in the p75(NTR) cholinergic basal forebrain septohippocampal pathway.Exp Neurol. 2001 Aug;170(2):227-43. doi: 10.1006/exnr.2001.7710. Exp Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11476589
-
Locus (coeruleus) minoris resistentiae in pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2014;11(10):992-1001. doi: 10.2174/1567205011666141107130505. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2014. PMID: 25387337 Review.
-
Alzheimer's disease: An evolving understanding of noradrenergic involvement and the promising future of electroceutical therapies.Clin Transl Med. 2021 Apr;11(4):e397. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.397. Clin Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33931975 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sleep is bi-directionally modified by amyloid beta oligomers.Elife. 2020 Jul 14;9:e53995. doi: 10.7554/eLife.53995. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32660691 Free PMC article.
-
Atp13a2-deficient mice exhibit neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, limited α-synuclein accumulation and age-dependent sensorimotor deficits.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 May 15;22(10):2067-82. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt057. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23393156 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of β2-adrenergic receptors prevents AD-type synaptotoxicity via epigenetic mechanisms.Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Nov;28(11):4877-4888. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02145-5. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37365243
-
The interaction between neurotransmitter receptor activity and amyloid-β pathology in Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2025 Jul;106(2):391-409. doi: 10.1177/13872877251342273. Epub 2025 Jul 1. J Alzheimers Dis. 2025. PMID: 40388923 Review.
-
Dysfunctional Sensory Modalities, Locus Coeruleus, and Basal Forebrain: Early Determinants that Promote Neuropathogenesis of Cognitive and Memory Decline and Alzheimer's Disease.Neurotox Res. 2016 Oct;30(3):295-337. doi: 10.1007/s12640-016-9643-3. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Neurotox Res. 2016. PMID: 27339162 Review.
References
-
- Berg L, McKeel DW, Jr, Miller JP, Storandt M, Rubin EH, Morris JC, Baty J, Coats M, Norton J, Goate AM, Price JL, Gearing M, Mirra SS, Saunders AM. Clinicopathologic studies in cognitively healthy aging and Alzheimer’s disease: relation of histologic markers to dementia severity, age, sex, and apolipoprotein E genotype. Arch Neurol. 1998;55(3):326–335. doi: 10.1001/archneur.55.3.326. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Borchelt DR, Ratovitski T, van Lare J, Lee MK, Gonzales V, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Price DL, Sisodia SS. Accelerated amyloid deposition in the brains of transgenic mice coexpressing mutant presenilin 1 and amyloid precursor proteins. Neuron. 1997;19(4):939–945. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80974-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
